Mastering Observability: The 7 Factors Every Enterprise Should Know
- Oct 23, 2023
- Blogs
- 5 min read
As digital journeys grow in complexity and volume, and distributed and cloud computing reshape the monitoring landscape, one thing is clear: Application Performance Monitoring (APM) is no longer the go-to solution, and Observability is the way forward. The days of merely collecting system-wide metrics from the bottom up and manually monitoring static performance thresholds are behind us. Today, it is all about adopting a top-down approach that examines interactions among various transaction participants, with a strong focus on extracting business insights and enhancing customer satisfaction.
To help you navigate this exciting shift in monitoring, we’ve compiled a list of seven crucial considerations for selecting the perfect observability platform for your enterprise. Whether you’re new to the world of full-stack observability, or looking to upgrade your current setup, these insights will prove invaluable in making an informed choice. Let’s dive in!
![]()
1. Observability Pipeline
An observability solution for multi-party digital journeys should be flexible and hyper-configurable to work with data adapters on a multitude of sources, especially logs and business traces. It should provide a unified view of data spread across multiple disparate silos. Most importantly, it must be able to handle data at scale, with big data infrastructure for AIOps and MLOps, since manually analyzing data at the volume and velocity expected in modern enterprises is virtually impossible.
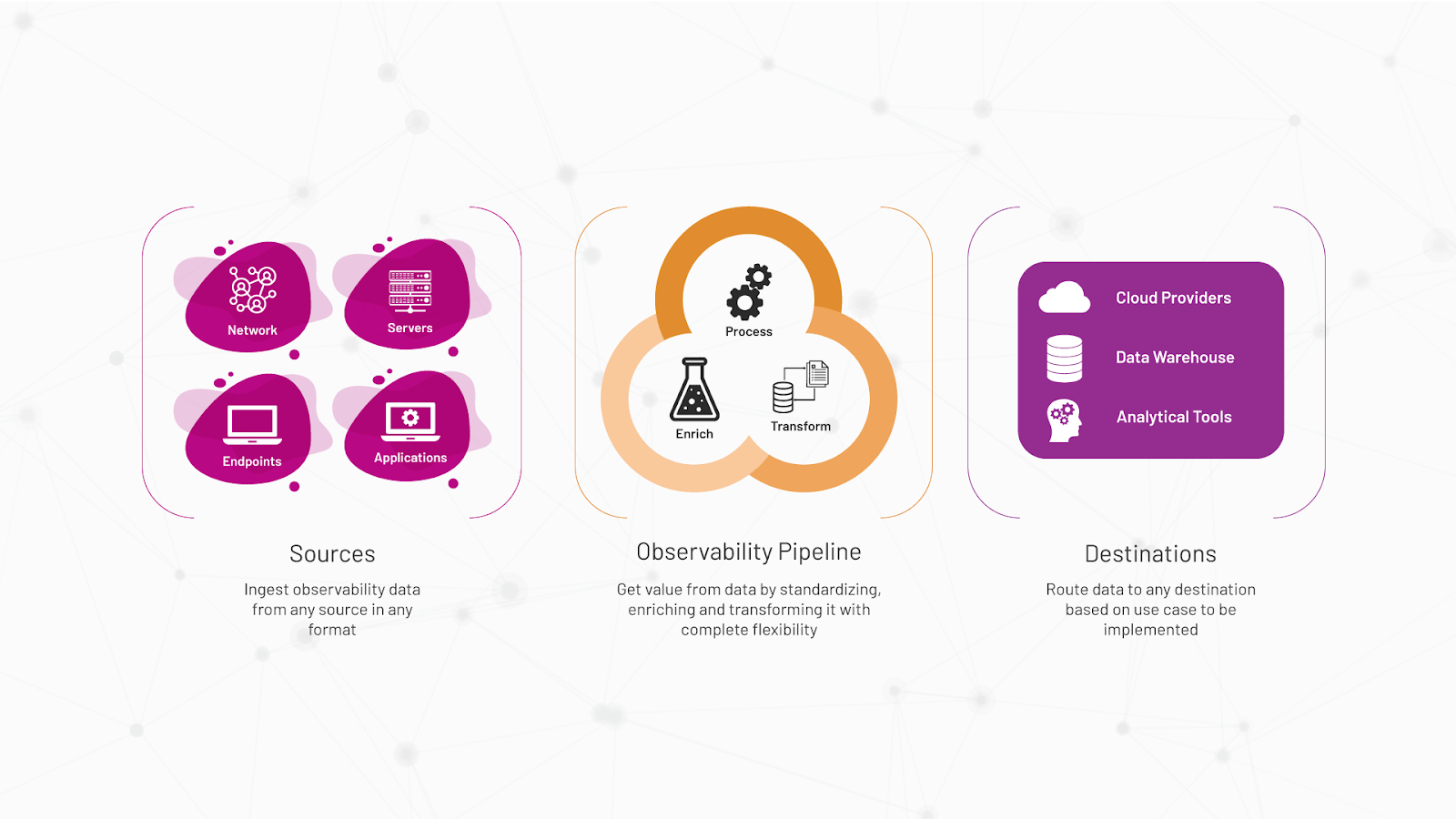
In order to protect existing tool investments and avoid vendor lock-in, an observability pipeline should be based on open standards like OpenTelemetry, scaling effortlessly and demanding minimal data standardization and integration efforts with existing pipelines. Moreover, it should serve as a central data hub, securely storing and ensuring swift access to your data for visualization, notifications, and analytics—all consolidated in one location. What’s more, it should be crafted with your future in mind. As your enterprise grows, this observability pipeline should effortlessly adapt to accommodate expanding data volumes and evolving requirements. From merely an observability tool, it then evolves into a Single Source of Truth: a data lake for all your business and operational data.
![]()
2. Comprehensive Real-time Observability
Traditional APMs typically employ a bottom-up approach, gathering metrics from infrastructure, network, and function calls, which are later sampled and stored for post-facto root cause analysis (RCA). In contrast, observability flips the script, adopting a top-down perspective. It begins with user context, pinpointing problematic steps that trigger real-time system views. Each component provides IT Operations Teams with relevant information specific to the issue at hand.
![]()
3. Customer-Centric Top-down Driven Insights
When it comes to tracking customer journeys in the digital realm—whether it’s in payments, lending, rewards programs, or e-commerce—the ability to gain deeper business insights through observability is paramount. What truly aligns an Observability platform with the customer experience is its ability to assess how IT errors can impact critical business KPIs.
The business metadata overlaid on tracing data allows operational dashboards to become customer-centric, intelligent, and more contextual, allowing a business-flow-based cross-tier integrated view of transactions across multiple silos. Real-time failure dashboards display the technical and business failures for journeys along with the failure touchpoint and possible recommendations for resolution. These unified views fuel a deeper understanding of micro-journey states to assess current or potential business impact, and handle scale at real-time to seamlessly transition from a summarized and aggregated view to individual journey behaviour. This shift towards a customer-centric perspective empowers organizations to gain deeper, context-rich insights into their systems, enabling decision making and quick responses and enhancing both operational efficiency and customer experience.
![]()
4. Empowering Customer Support
In today’s world, where delivering an exceptional user experience is paramount, the customer support function shoulders the critical responsibility of swiftly addressing and resolving customer complaints. This necessitates personalized dashboards with advanced query capabilities encompassing a wide array of IT and business parameters.
![]()
To meet this need, an observability solution must introduce traceability— mapping the entire customer journey across diverse touchpoints – to streamline customer service, dispute resolution, and compliance tasks. Traceability equips you with the ability to effortlessly pinpoint problematic business flows using criteria such as transaction IDs, merchant IDs, API names, or error codes. IT Operations teams can then isolate failure points, uncover root causes, and extract data for compliance reporting or in-depth incident investigations.
![]()
5. Enhancing Stakeholder Collaboration
In a DevOps world, developers own the responsibility for the operations of their applications. Any observability solution selected for distributed and microservice-based architectures should provide workflows aligned with how multiple distributed, interdependent engineering teams are operating. A good observability back-end should allow Site Reliability Engineers (SREs) and DevOps personnel who are not familiar with all aspects of an application to troubleshoot a production issue quickly and intuitively even with no domain knowledge.
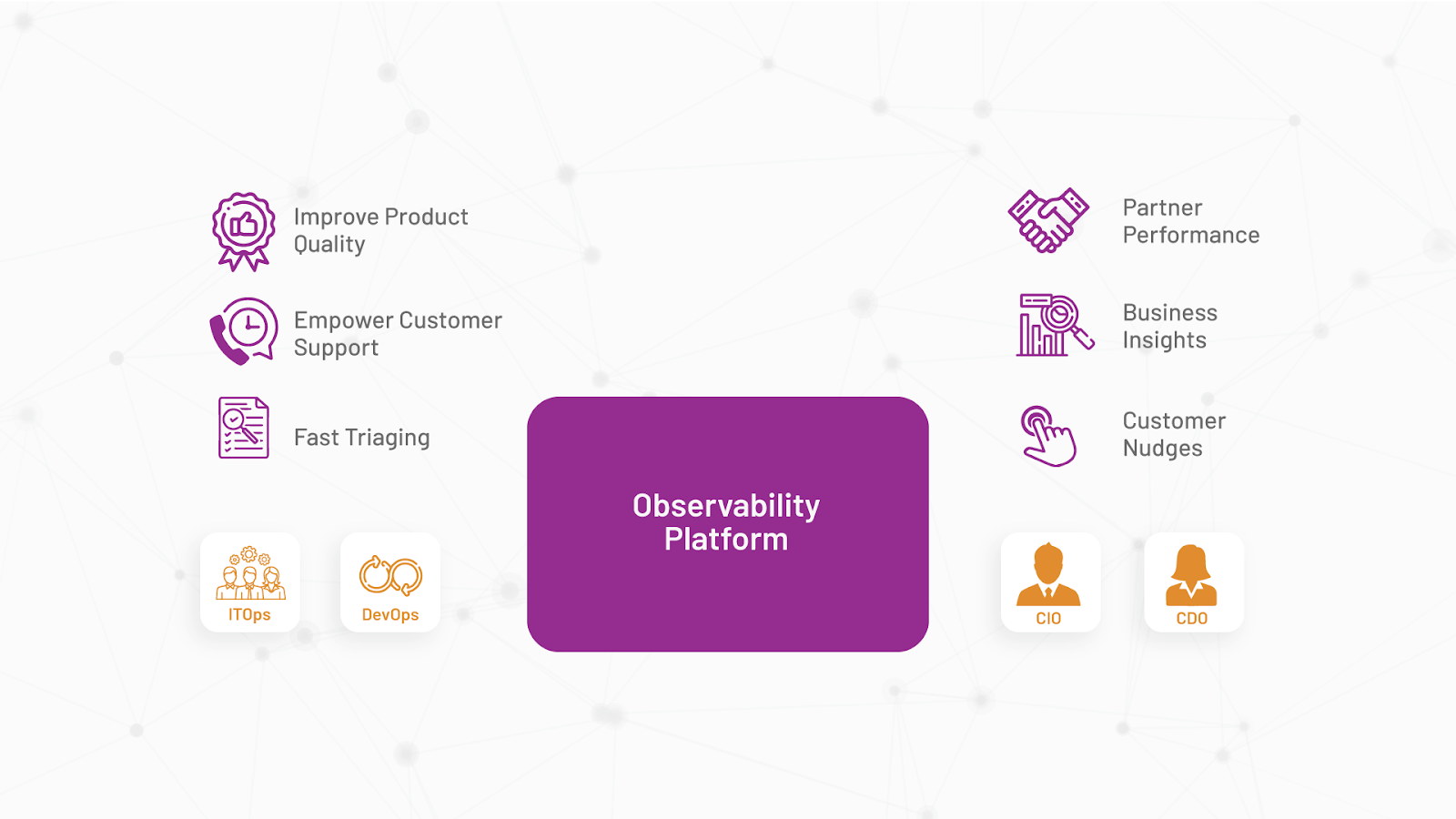
At the same time, the business leaders should be presented with meaningful, observability-driven KPIs to get a user-centric view of business journeys. These help CXOs benchmark their systems against competition, accelerate decision-making and improve customer experience and partner interactions in real-time.
![]()
6. Data Security
Observability platforms collect and store vast amounts of data, including logs, metrics, and traces, which may contain sensitive information. Ensuring the security of this data is crucial to prevent data breaches, unauthorized access, or leaks. Many industries have strict regulatory requirements that govern data privacy and security. Choosing an observability platform that complies with these regulations is essential to avoid legal and financial consequences. Controlling who has access to observability data is also vital. The solution should provide robust access control mechanisms, including role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA), to restrict access to authorized personnel only.
![]()
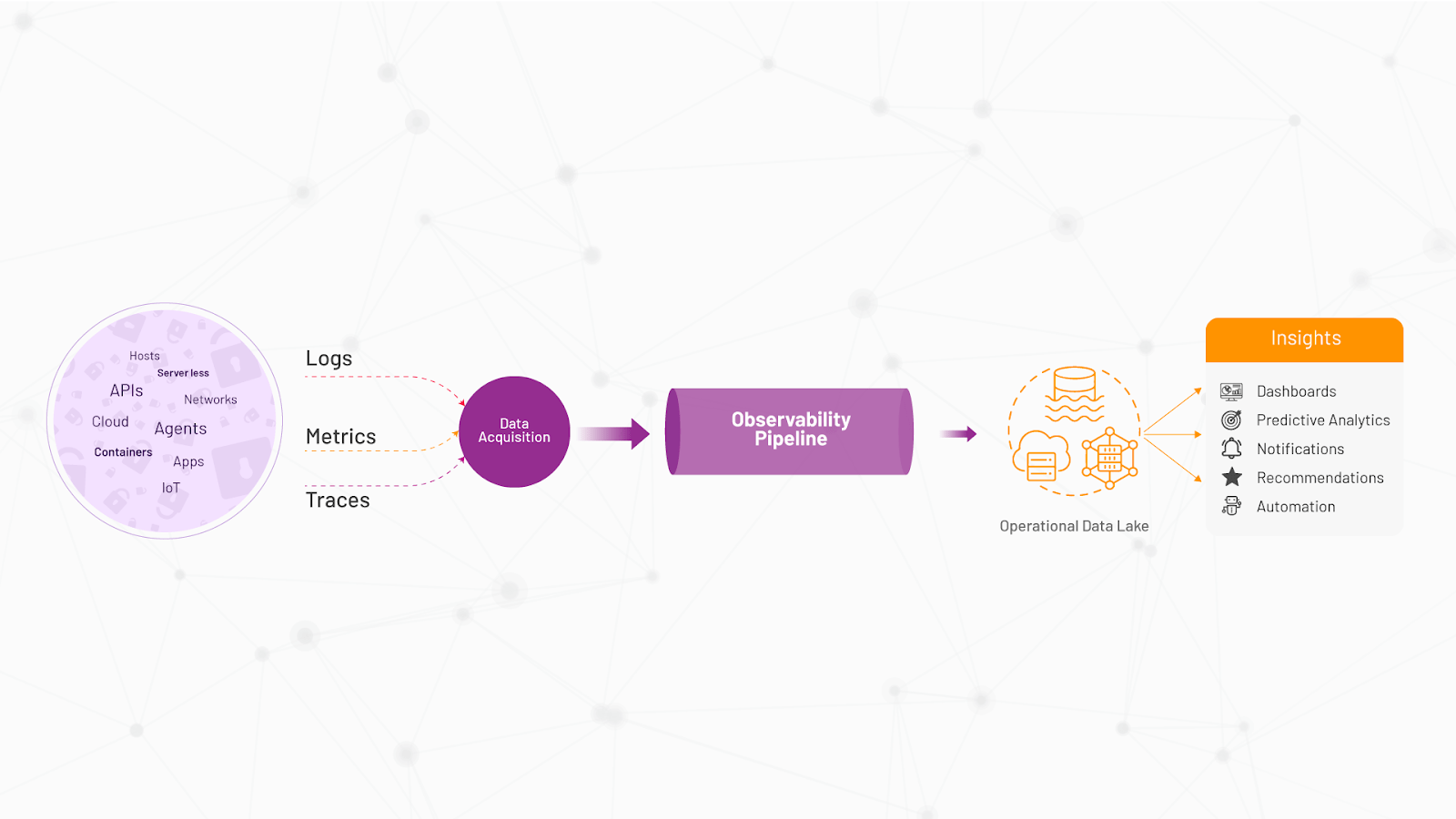
7. Future-proof AIOps Strategy
An ideal observability tool should enable an organization to transition to the Holy Grail of Incident Management – reduced MTTD (Mean Time to Detect) and MTTR (Mean Time to Resolve) eventually leading to pre-emptive detection and automated resolution of issues. This is possible if the platform provides an operational data lake that lends itself to the development of machine learning techniques and AI-powered algorithms to learn expected system behaviour, detect and alert on anomalous journeys, and accelerate root cause analysis. This opens doors to complementary use cases like automated capacity planning, self-ticketing, and integration with ITSM systems to automate issue resolution workflows.
![]()
In summary, the objective of this checklist is to ensure that not only does your chosen observability platform empower you with business insights into your digital journeys, but also equips you to chart a course toward operational excellence!
To know more about how VuNet can partner with you on this journey, reach out to us at [email protected] .