vuApp360 Deployment & Configuration
vuSmartMaps Configuration: Enabling Distributed Traces Telemetry
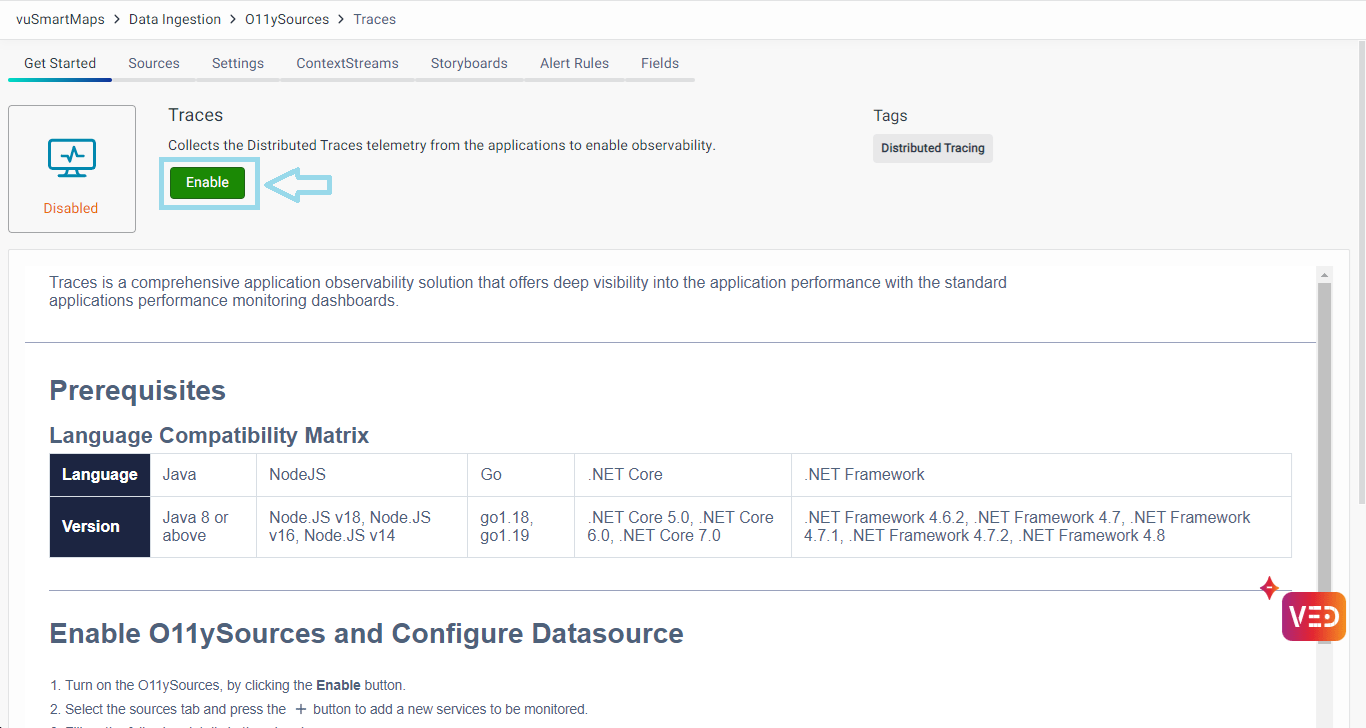
Traces O11ySource collects Distributed Traces telemetry from applications to provide comprehensive observability, offering deep insights into application performance through standard applications performance monitoring dashboards.
Enabling Traces O11ySource
- Navigate to O11ySources:
- vuSmartMaps O11ySources can be accessed by navigating from the left navigation menu (Data Ingestion > O11ySources).
- Locate Traces O11ySource on the landing page.

- Enable Traces O11ySources:
- Click the Enable button to activate Traces O11ySource.

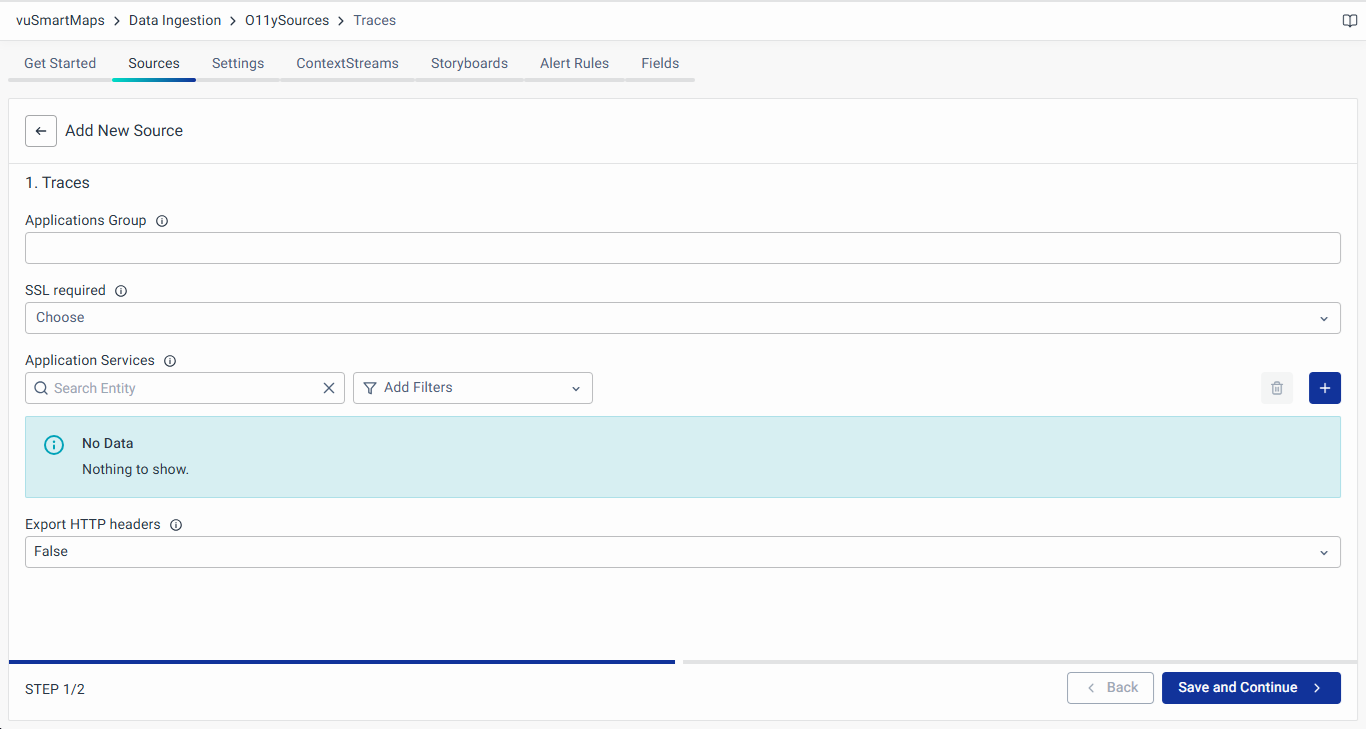
Configuring Data Sources
- Navigate to the Sources tab and click the + button to add new services to be monitored.
- Fill up the Following Details in the Wizard:
- Applications Group: Name of the application group.
- SSL Required: If Yes, TLS will be turned ON.
- Application Services: Specify the name of your application and service that will be displayed in the observability UI. In a microservices architecture, an application can consist of multiple services. However, in the absence of microservices, each application would typically have just one service. It is possible to have the same name for both the application and service if desired.
- Language: The programming language used for developing the application service: Java, NodeJS, .NET, GoLang.
- Application Name: Name of the target application.
- Service Name: Service name in the application. Typically in monolithic applications, the service name and application name are the same. In the microservices application, there would be one application that can have one or more services.
- Export HTTP Header (True/False): Enable this field, if HTTP Header is required to be captured.
- Download the client instrumentation package for the selected language from the agent configuration wizard.

- Follow the instructions provided in the client instrumentation package.
Following these steps, you have successfully enabled Traces O11ySource and configured the data sources for real-time application performance monitoring.
Configuring Sampling Policies
Sampling configuration allows the system to selectively decide on which traces to store. This helps in reducing the amount of data kept in the system.
There are two types of sampling policies that can be configured for traces:
- Global Policies: Apply to all types of traces coming into the system.
- Service-Specific Policies: Apply to a specific set of services.
A separate page for sampling-related configurations is introduced. These configurations are controlled from the Settings tab on the Traces O11ySource page. The Settings tab includes three sections:
- Sampling Policy
Defines policies for deciding which traces to store. Policies can use inline rules or refer to rules defined in the Sampling Rules section. - Sampling Rule
Provides a way to define individual rules that can be referred to in Sampling Policies to form compound rules. - Additional Configuration
Controls data enrichments and transformations on received traces using optional YAML configurations.

The dashboards provided in vuApp360 are designed to display pre-sampled data.
Sampling Policy
Sampling Policies configured here allow vuSmartMaps to intelligently decide on which traces to store, helping to reduce the amount of data kept in the system by selecting only important traces. This is an optional functionality. If no sampling policies are configured, vuSmartMaps will store 100% of the traces collected.
Sampling policies can use rules defined inline within them or refer to rules defined in the Sampling Rules section. Using rules from sampling rules in policies enables users to define compound policies that can refer to more than one rule. When multiple sampling policies are configured, vuSmartMaps will apply all the policies to all traces received and will take a final decision based on the following:
- The trace is dropped when there is one explicit 'Do not sample' decision based on an inverted match.
- The trace is stored when there is one 'Sample' decision.
- The trace is stored when there is one 'Sample' decision based on an inverted match and there are no 'Do not sample' decisions.
- The trace is dropped in all other cases.
To configure a new sampling policy, use the + button and provide the following details in the modal:

- Policy Name: Unique name assigned by the user.
- Scope: Specify whether the policy applies to all traces (Global) or to a specific set of services. Options include All, For These Services, For Services Except These.
- Definition Type: Choose to define the policy details inline or refer to a rule defined in the Sampling Rules Section.
- Inline: If this option is selected, the configured policy type becomes applicable:
- Policy Type: Specify the type of sampling policy. vuSmartMaps offers following seven policy types:
- Allow All: Marks all traces received to be stored.
- Data Rate: Tracks spans per second rate of traces and drops traces beyond the configured threshold.
- Spans per Second: Maximum number of spans that can be processed each second.
- Latency: Stores only those traces with latency greater than the configured threshold.
- Threshold in Milliseconds: Only traces with latency greater than the given threshold (in ms) will be allowed.
- Number Attribute: Stores only those traces with the value of the configured attribute falling within a specified range.
- Attribute: Select the attribute key to match data received from applications (e.g., HTTP Status Code).
- Minimum Value: Enter the minimum acceptable value (e.g., 400 for HTTP Status codes).
- Maximum Value: Enter the maximum acceptable value (e.g., 500 for HTTP Status codes).
- Percentage: Stores only a specified percentage of traces received, dropping the rest.
- Sampling Percentage: The percentage rate at which traces are sampled.
- Status: Stores traces with specified statuses, dropping the rest.
- Status Type: Status value for which traces will be retained. Options: Error, OK, Unset.
- String Attribute: Stores only those traces with the value of a configured attribute matching the configured condition.
- Attribute: Select the attribute key to match data received from applications (e.g., Application, Service Name, Host Name, HTTP Host, HTTP Target, HTTP Route, HTTP URL, DB Name, DB System, Messaging System, Transaction).
- Values: Enter the values to match against (e.g., health, metrics, etc.).
- Regular Expression: When 'True', the system will match the attribute values by regular expression string.
- Invert Match: When 'True', the system will reverse the match condition.
- Use Predefined Rule Sets: If this option is selected, choose one of the following policy types and select the relevant rules from the Sampling Rules section:
- AND of Multiple Rules: Build a compound rule with an AND of multiple rules defined in the Sampling Rules section.
- Rate Distribution: Allocate portions of the total allowed rate to a set of rules from the Sampling Rules Section. Traces matching each rule will be allocated a portion of the total rate allowed.
- Single Rule: Use a single rule defined in the Sampling Rules section.
Sampling Rule
Sampling rules provide a way to define individual rules that can be referred to in Sampling Policies to form compound rules. The rules defined in Sampling Rules are not used unless referred to by a policy in Sampling Policies. Using rules from Sampling Rules in policies enables users to define compound policies that can refer to more than one rule.
To configure a new sampling rule, use the + button and provide the following details in the modal:
- Rule Name: Unique name assigned by the user.
- Rule Type: Specify the type of sampling rule. vuSmartMaps offers seven predefined rule types (as explained above for inline policy types).

Additional Configuration
The Additional Configuration section can be used to control data enrichments and transformations done on traces received. Users can add optional YAML configurations. Below is an example:
transform:
trace_statements:
- context: span
statements:
- set(attributes["instrumentation_library_name"], instrumentation_scope.name)
- set(attributes["library"], attributes["db.system"])
- set(attributes["library"], attributes["messaging.system"])
- set(attributes["library"], "Express") where instrumentation_scope.name == "@opentelemetry/instrumentation-express"
- set(attributes["library"], "MongoDB") where instrumentation_scope.name == "io.opentelemetry.mongo-3.1"
- set(attributes["library"], "Go-kit") where instrumentation_scope.name == "go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/instrumentation/github.com/go-kit/kit/otelkit"
- set(attributes["library"], "RabbitMQ") where instrumentation_scope.name == "io.opentelemetry.rabbitmq-2.7"
- set(attributes["library"], "NodeJS HTTP Client / Server") where instrumentation_scope.name == "@opentelemetry/instrumentation-http"
- set(attributes["library"], "Redis") where instrumentation_scope.name == "@opentelemetry/instrumentation-redis"
- set(attributes["library"], "Spring MVC") where instrumentation_scope.name == "io.opentelemetry.spring-webmvc-3.1"
- set(attributes["library"], "Tomcat") where instrumentation_scope.name == "io.opentelemetry.tomcat-7.0"
- set(attributes["library"], "Servlet") where instrumentation_scope.name == "io.opentelemetry.servlet-3.0"
- set(attributes["library"], attributes["db.system"]) where instrumentation_scope.name == "io.opentelemetry.jdbc"
- set(attributes["library"], "Spring Data") where instrumentation_scope.name == "io.opentelemetry.spring-data-1.8"
- set(attributes["library"], "Hibernate") where instrumentation_scope.name == "io.opentelemetry.hibernate-4.0"
- set(attributes["library"], "Go HTTP Client / Server") where instrumentation_scope.name == "go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/instrumentation/net/http/otelhttp"
- set(attributes["library"], "Spring Scheduling") where instrumentation_scope.name == "io.opentelemetry.spring-scheduling-3.1 1.14.0-alpha"
- set(attributes["destination"], attributes["db.system"])
- set(attributes["destination"], attributes["messaging.system"])
- set(attributes["destination"], attributes["net.peer.name"])
- set(attributes["destination"], replace_match(attributes["http.url"], "https?://[^/]+/([^/]+)", "$1"))
- set(attributes["transaction"], Concat([attributes["http.method"], attributes["http.target"]], " ")) where (attributes["http.target"] != nil and attributes["http.method"] != nil and attributes["http.target"] != "")
- set(attributes["transaction"], Concat([attributes["http.method"], attributes["http.route"]], " ")) where (attributes["http.route"] != nil and attributes["http.method"] != nil and attributes["http.route"] != "")
- set(attributes["site"], "default")
This configuration enriches and transforms trace data, making it more meaningful and useful for analysis.
The Settings tab for Traces O11ySource provides a centralized location for configuring sampling policies, rules, and additional configurations. This setup simplifies the process, reduces user confusion, and enhances the ability to manage and control the data stored in the system effectively. By intelligently sampling traces, users can ensure that they are storing only the most relevant and important data, optimizing both storage and analysis capabilities.
Client Side Traces Instrumentation

- Java
- C# / .NET
- Go
- Kubernetes
- Node.js
- Python
- NGINX
Instrumentation Process
SpringBoot / jar
Steps to instrument the java application running as a SpringBoot / jar:
-
Download the client instrumentation package from the O11ysource, which contains the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar.- Place the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jarin your preferred directory.
- Place the
-
Launch the application with the following configuration
java -javaagent:path/to/vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar
-Dotel.resource.attributes=application=<APPLICATION_NAME>
-Dotel.service.name=<SERVICE_NAME> -Dotel.metrics.exporter=none
-Dotel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=<TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT> -jar app.jar -
Ensure to update the following before using this command.
APPLICATION_NAME: Change it to match your application name.SERVICE_NAME: Change it to match the service name (microservices) or application layer (monolithic)TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT: Change it to match the URL of the vuSmartMaps.- This should be http://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4317.
Example:
- Here, the vuSmartMaps is running in the host with IP 10.0.0.1
java -javaagent:vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar
-Dotel.resource.attributes=application=UPI -Dotel.service.name=upi-switch
-Dotel.metrics.exporter=none -Dotel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=http://10.0.0.1:4317 -jar upi.jar
JBoss / WildFly (Standalone Mode) in Linux
Steps to instrument the java application running in JBoss / WildFly (Standalone Mode) in Linux:
-
Download the client instrumentation package, which contains the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar.- Place the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jarin your preferred directory.
- Place the
-
Edit the
<JBOss_HOME>/bin/standalone.conffile and update theJAVA_OPTSenvironment variableJAVA_OPTS="-javaagent:path/to/vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar -Dotel.resource.attributes=application=<APPLICATION_NAME> -Dotel.service.name=<SERVICE_NAME> -Dotel.metrics.exporter=none -Dotel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=<TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT>" -
Ensure to update the following before using this command.
APPLICATION_NAME: Change it to match your application nameSERVICE_NAME:- Change it to match the service name (microservices) or application layer (monolithic).
- When multiple war files are running in a single JBoss / Wildfly server, then enable the auto discovery of service name using the argument
-Dotel.service.name=FROM_WEB_CONTEXT
TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT: Change it to match the URL of the vuSmartMaps. It should be http://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4317
Example:
JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -javaagent:D:\Dev\OTel\auto_instrumentation_package_java\otel-lib\vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar -Dotel.resource.attributes=application=APPLICATION_NAME -Dotel.service.name=SERVICE_NAME -Dotel.metrics.exporter=none -Dotel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=http://localhost:4317" -
Restart JBoss
JBoss / WildFly (Domain Mode) in Linux
Steps to instrument the java application running in JBoss / WildFly (Domain Mode) in Linux:
-
Download the client instrumentation package, which contains the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar.- Place the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jarin your preferred directory.
- Place the
-
Edit the
<JBOss_HOME>/bin/domain.conffile and update theJAVA_OPTSenvironment variableJAVA_OPTS="-javaagent:path/to/vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar -Dotel.resource.attributes=application=<APPLICATION_NAME> -Dotel.service.name=<SERVICE_NAME> -Dotel.metrics.exporter=none -Dotel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=<TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT>" -
Ensure to update the following before using this command.
APPLICATION_NAME: Change it to match your application nameSERVICE_NAME:- Change it to match the service name (microservices) or application layer (monolithic).
- When multiple war files are running in a single JBoss / Wildfly server, then enable the auto discovery of service name using the argument
-Dotel.service.name=FROM_WEB_CONTEXT
TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT: Change it to match the URL of the vuSmartMaps. It should be http://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4317.
Example:
JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -javaagent:D:\Dev\OTel\auto_instrumentation_package_java\otel-lib\vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar -Dotel.resource.attributes=application=APPLICATION_NAME -Dotel.service.name=SERVICE_NAME -Dotel.metrics.exporter=none -Dotel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=http://localhost:4317" -
Restart JBoss
JBoss / WildFly (Standalone Mode) in Windows
Steps to instrument the java application running in JBoss / WildFly (Standalone Mode) in Windows:
-
Download the client instrumentation package, which contains the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar.- Place the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jarin your preferred directory.
- Place the
-
Edit the
<JBOss_HOME>/bin/standalone.conf.batfile and update theJAVA_OPTSenvironment variableJAVA_OPTS="-javaagent:path/to/vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar -Dotel.resource.attributes=application=<APPLICATION_NAME> -Dotel.service.name=<SERVICE_NAME> -Dotel.metrics.exporter=none -Dotel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=<TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT>" -
Ensure to update the following before using this command.
APPLICATION_NAME: Change it to match your application nameSERVICE_NAME:- Change it to match the service name (microservices) or application layer (monolithic).
- When multiple war files are running in a single JBoss / Wildfly server, then enable the auto discovery of service name using the argument
-Dotel.service.name=FROM_WEB_CONTEXT
TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT: Change it to match the URL of the vuSmartMaps. It should be http://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4317.
Example:
set "JAVA_OPTS=%$JAVA_OPTS% -javaagent:D:\Dev\OTel\auto_instrumentation_package_java\otel-lib\vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar -Dotel.resource.attributes=application=APPLICATION_NAME -Dotel.service.name=SERVICE_NAME -Dotel.metrics.exporter=none -Dotel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=http://localhost:4317" -
Restart JBoss
JBoss / WildFly (Domain Mode) in Windows
Steps to instrument the java application running in JBoss / WildFly (Domain Mode) in Windows:
-
Download the client instrumentation package, which contains the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar.- Place the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jarin your preferred directory.
- Place the
-
Edit the
<JBOss_HOME>/bin/domain.conf.batfile and update theJAVA_OPTSenvironment variableJAVA_OPTS="-javaagent:path/to/vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar -Dotel.resource.attributes=application=<APPLICATION_NAME> -Dotel.service.name=<SERVICE_NAME> -Dotel.metrics.exporter=none -Dotel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=<TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT>" -
Ensure to update the following before using this command.
APPLICATION_NAME: Change it to match your application nameSERVICE_NAME:- Change it to match the service name (microservices) or application layer (monolithic).
- When multiple war files are running in a single JBoss / Wildfly server, then enable the auto discovery of service name using the argument
-Dotel.service.name=FROM_WEB_CONTEXT
TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT: Change it to match the URL of the vuSmartMaps. It should be http://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4317.
Example:
set "JAVA_OPTS=%$JAVA_OPTS% -javaagent:D:\Dev\OTel\auto_instrumentation_package_java\otel-lib\vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar -Dotel.resource.attributes=application=APPLICATION_NAME -Dotel.service.name=SERVICE_NAME -Dotel.metrics.exporter=none -Dotel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=http://localhost:4317" -
Restart JBoss
Apache Tomcat running on Linux
Steps to instrument the java application running in Apache Tomcat running on Linux
-
Download the client instrumentation package, which contains the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar.- Place the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jarin your preferred directory.
- Place the
-
Edit the
setenv.shin the bin directory of Tomcat and add the following content.- Create the
setenv.shin the bin directory if it doesn't existexport CATALINA_OPTS="$CATALINA_OPTS -javaagent:path/to/vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar"
export OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT=<TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT>
export OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES=application=<APPLICATION_NAME>
export OTE_SERVICE_NAME=<SERVICE_NAME>
export OTEL_METRICS_EXPORTER=none
- Create the
-
Ensure to update the following before using this command.
APPLICATION_NAME: Change it to match your application nameSERVICE_NAME:- Change it to match the service name (microservices) or application layer (monolithic).
- When multiple war files are running in a single Apache Tomcat server, then enable the auto discovery of service name using the argument
-Dotel.service.name=FROM_WEB_CONTEXT
TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT: Change it to match the URL of the vuSmartMaps. It should be http://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4317
-
Restart Apache Tomcat
Apache Tomcat running on Windows
Steps to instrument the java application running in Apache Tomcat running on Windows:
-
Download the client instrumentation package, which contains the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar.- Place the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jarin your preferred directory.
- Place the
-
Edit the
setenv.batin the bin directory of Tomcat and add the following content.- Create the
setenv.batin the bin directory if it doesn't existset "CATALINA_OPTS=%CATALINA_OPTS% -javaagent:path\to\vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar"
set "OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT=<TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT>"
set "OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES=application=<APPLICATION_NAME> -Dotel.service.name=<SERVICE_NAME>"
set "OTEL_METRICS_EXPORTER=none"
- Create the
-
Ensure to update the following before using this command.
APPLICATION_NAME: Change it to match your application nameSERVICE_NAME:- Change it to match the service name (microservices) or application layer (monolithic).
- When multiple war files are running in a single Apache Tomcat server, then enable the auto discovery of service name using the argument
-Dotel.service.name=FROM_WEB_CONTEXT
TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT: Change it to match the URL of the vuSmartMaps. It should be http://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4317
-
Restart Apache Tomcat
Weblogic (Standalone Weblogic Servers)
Steps to instrument the java application running in a standalone Weblogic server:
-
Download the client instrumentation package, which contains the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar.- Place the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jarin your preferred directory.
- Place the
-
Edit
startWebLogic.shlocated at<weblogic_<version#>_install_dir>/user_projects/domains/<domain_name>/bin/startWebLogic.sh.- Add the following to the beginning of your application server start script
export JAVA_OPTIONS="$JAVA_OPTIONS -javaagent:path/to/vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar -Dotel.resource.attributes=application=<APPLICATION_NAME> -Dotel.service.name=<SERVICE_NAME> -Dotel.metrics.exporter=none -Dotel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=<TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT>"
- Add the following to the beginning of your application server start script
-
Ensure to update the following before using this command.
APPLICATION_NAME: Change it to match your application nameSERVICE_NAME:- Change it to match the service name (microservices) or application layer (monolithic).
- When multiple war files are running in a single Weblogic server, then enable the auto discovery of service name using the argument
-Dotel.service.name=FROM_WEB_CONTEXT
TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT: Change it to match the URL of the vuSmartMaps. It should be http://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4317
-
Restart Weblogic
Weblogic (Servers managed by Admin Console)
Steps to instrument the java application running in clustered Weblogic server where the admin console is used to manage the instance:
-
Download the client instrumentation package, which contains the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar.- Place the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jarin your preferred directory.
- Place the
-
For clustered WebLogic servers, you start and stop using Node Manager and configure server startup in the WebLogic Server Administration Console.
-
Open the WebLogic Server Administration Console.
-
Navigate to Environment > Servers and click your server in the Server List
-
Click the Server Start tab.
-
Add the javaagent argument and set the value to the path to the Java Agent
-javaagent:path/to/vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar -Dotel.resource.attributes=application=<APPLICATION_NAME> -Dotel.service.name=<SERVICE_NAME> -Dotel.metrics.exporter=none -Dotel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=<TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT> -Dotel.exporter.otlp.compression=gzip -
Please update the following before using this command.
APPLICATION_NAME: Change it to match your application nameSERVICE_NAME:- Change it to match the service name (microservices) or application layer (monolithic).
- When multiple war files are running in a single Weblogic server, then enable the auto discovery of service name using the argument
-Dotel.service.name=FROM_WEB_CONTEXT
TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT: Change it to match the URL of the vuSmartMaps. It should be http://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4317
-
Restart the Weblogic managed server

Websphere Application Server ND
Steps to instrument the java application running in Websphere Application Server Network Deployment:
-
Download the client instrumentation package which contains the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar.- Place the
vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jarin your preferred directory.
- Place the
-
Log in to the WebSphere Integrated Solutions Console
-
Navigate to Servers > Server type > WebSphere application servers.
-
Select the server.
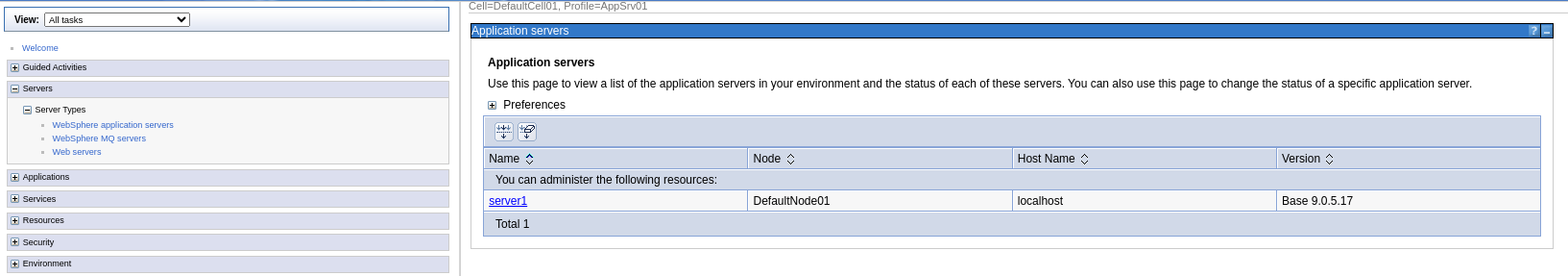
-
Go to Java and Process Management > Process Definition.

-
Select Java Virtual Machine.
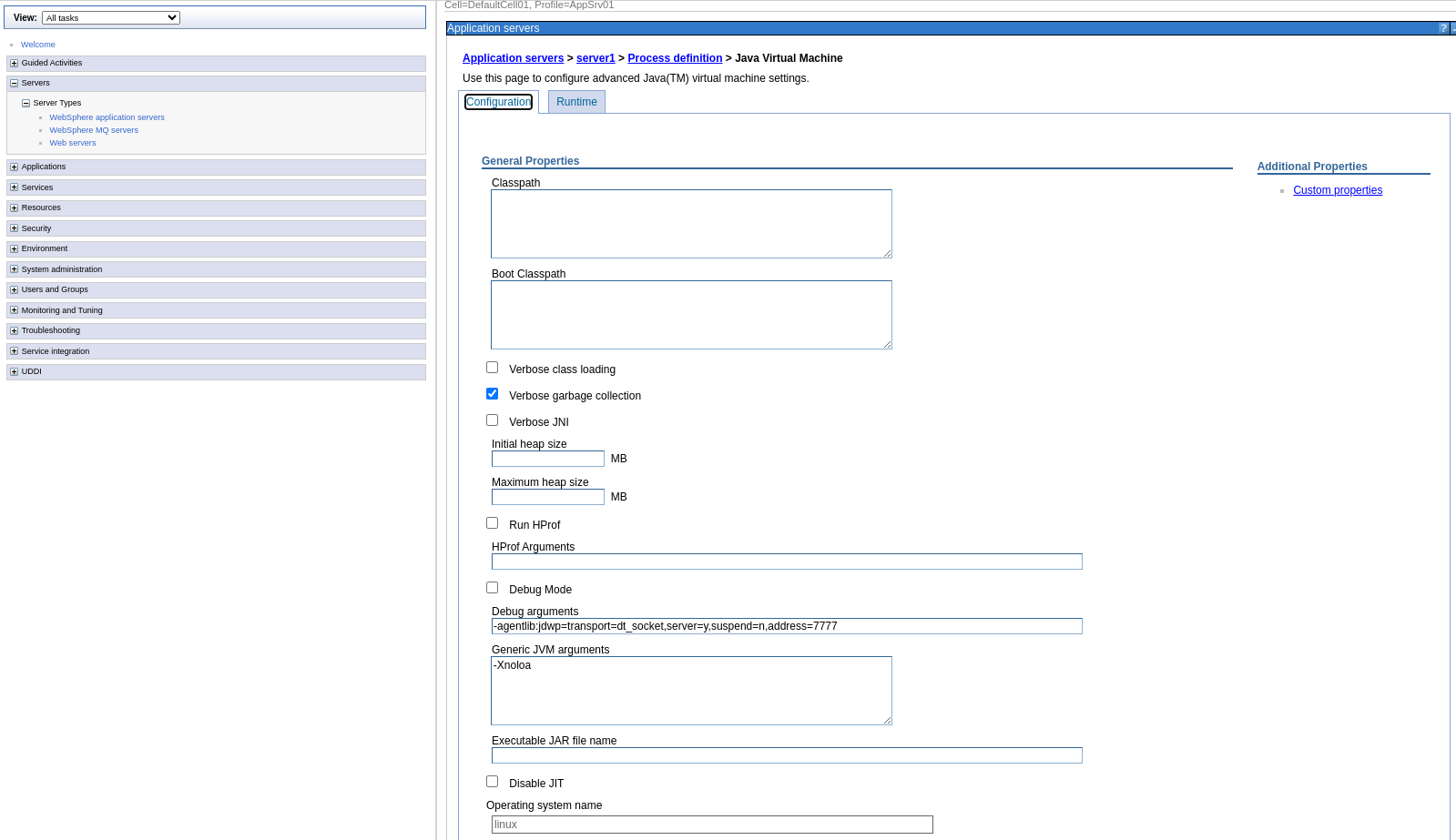
-
In Generic JVM arguments, add the following arguments.
-javaagent:path/to/vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar -Dotel.resource.attributes=application=<APPLICATION_NAME> -Dotel.service.name=<SERVICE_NAME> -Dotel.metrics.exporter=none -Dotel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=<TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT> -Dotel.exporter.otlp.compression=gzip -
Please update the following before saving the configuration
APPLICATION_NAME: Change it to match your application nameSERVICE_NAME:- Change it to match the service name (microservices) or application layer (monolithic).
- When multiple war files are running in a single Weblogic server, then enable the auto discovery of service name using the argument
-Dotel.service.name=FROM_WEB_CONTEXT
TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT: Change it to match the URL of the vuSmartMaps. It should be http://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4317
-
Save the configuration and restart the server.
Docker
If your application is running in Docker, then modify the Dockerfile to include the JVM parameters mentioned above.
See the extract from a sample Dockerfile.
COPY ./vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar /usr/local/lib/vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar
ENV JAVA_TOOL_OPTIONS "-javaagent:/usr/local/lib/vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar"
ENV OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES "application=<Application Name>"
ENV OTEL_SERVICE_NAME "<Service Name>"
ENV OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT "<TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT>"
ENV OTEL_METRICS_EXPORTER "none"
ENTRYPOINT ["java","-Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/urandom","-jar","./app.jar", "--port=80"]
If you don’t want to rebuild the container, then you can re-run the container with the following additional environment variables.
docker run -d \
-v ./vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar:/app/opentelemetry-javaagent.jar \
-e OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT=<TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT>\
-e OTEL_SERVICE_NAME=<Service Name> \
--entrypoint java \
-javaagent:/usr/local/lib/vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar \
-jar /app/myapp.jar
Ensure to update the following before using this command.
APPLICATION_NAME: Change it to match your application nameSERVICE_NAME: Change it to match the service name (microservices) or application layer (monolithic)TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT: Change it to match the URL of the vuSmartMaps. It should be http://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4317
Configuration
TLS Configuration
If the TLS is enabled on the vuSmartMaps traces receiver, please get the certificate from the server and configure the following additional parameters.
-Dotel.exporter.otlp.protocol=http/protobuf
-Dotel.exporter.otlp.certificate='/path/to/server/certificate'
The server certificate is included in the downloaded instrumentation package.
For the TLS case TRACES_INGESTION_ENDPOINT should be https://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4318
Capture HTTP Headers
In some applications, key transaction identifiers are passed as HTTP headers to the APIs. To capture these headers, additional instrumentation configurations are required. Below are the steps and examples for capturing HTTP headers for both HTTP servers and clients.
Capture HTTP Request Header for HTTP Server
To capture the request headers passed to a service, use the following configuration along with other instrumentation configurations mentioned in the previous sections.
OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_HTTP_SERVER_CAPTURE_REQUEST_HEADERS
You can configure one or more headers to be captured. If capturing multiple headers, separate them with commas.
An example is given below
java -javaagent:vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar
-Dotel.resource.attributes=application=UPI -Dotel.service.name=upi-switch
-Dotel.metrics.exporter=none -Dotel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=http://10.0.0.1:4317 -jar
-Dotel.instrumentation.http.server.capture-request-headers=client_id,txn_id
upi.jar
Capture HTTP Response Header for HTTP Server
To capture the response headers passed from a service, use the following configuration along with other instrumentation configurations mentioned in the previous sections.
OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_HTTP_SERVER_CAPTURE_RESPONSE_HEADERS
You can configure one or more headers to be captured. If capturing multiple headers, separate them with commas.
An example is given below
java -javaagent:vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar
-Dotel.resource.attributes=application=UPI -Dotel.service.name=upi-switch
-Dotel.metrics.exporter=none -Dotel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=http://10.0.0.1:4317 -jar
-Dotel.instrumentation.http.server.capture-response-headers=resp_code,resp_status
upi.jar
Capture HTTP Request Header for HTTP Client
To capture the request headers passed by a service, use the following configuration along with other instrumentation configurations mentioned in the previous sections.
OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_HTTP_CLIENT_CAPTURE_REQUEST_HEADERS
You can configure one or more headers to be captured. If capturing multiple headers, separate them with commas.
An example is given below
java -javaagent:vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar
-Dotel.resource.attributes=application=UPI -Dotel.service.name=upi-switch
-Dotel.metrics.exporter=none -Dotel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=http://10.0.0.1:4317 -jar
-Dotel.instrumentation.http.client.capture-request-headers=client_id,txn_id
upi.jar
Capture HTTP Response Header for HTTP Client
To capture the response headers received by a service, use the following configuration along with other instrumentation configurations mentioned in the previous sections
OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_HTTP_CLIENT_CAPTURE_RESPONSE_HEADERS
You can configure one or more headers to be captured. If capturing multiple headers, separate them with commas.
An example is given below
java -javaagent:vunet-opentelemetry-javaagent.jar
-Dotel.resource.attributes=application=UPI -Dotel.service.name=upi-switch
-Dotel.metrics.exporter=none -Dotel.exporter.otlp.endpoint=http://10.0.0.1:4317 -jar
-Dotel.instrumentation.http.client.capture-response-headers=resp_code,resp_status
upi.jar
Instrumentation Process
.NET Core 3.1 Application
-
The .NET Core 3.1 application does not support full auto instrumentation. It is partial auto instrumentation, which means code changes are required. The code changes are related to initializing the open telemetry.
-
Add the Open telemetry packages
<PackageReference Include="OpenTelemetry.Extensions.Hosting" Version="1.8.1" />
<PackageReference Include="OpenTelemetry.Exporter.Console" Version="1.8.1" />
<PackageReference Include="OpenTelemetry.Instrumentation.AspNetCore" Version="1.8.1" />
<PackageReference Include="OpenTelemetry.Instrumentation.Http" Version="1.8.1" />
<PackageReference Include="OpenTelemetry.Instrumentation.SqlClient" Version="1.8.0-beta.1" />
<PackageReference Include="OpenTelemetry.Instrumentation.Runtime" Version="1.8.0" />
<PackageReference Include="OpenTelemetry.Exporter.OpenTelemetryProtocol" Version="1.8.1" /> -
Add Open telemetry service. In the
Startup.csadd the below code
services.AddOpenTelemetry()
.ConfigureResource(resource => resource.AddService(serviceName))
.WithTracing(tracing => tracing
.AddAspNetCoreInstrumentation()
.AddHttpClientInstrumentation()
.AddOtlpExporter()
);
-
Make sure you include the required packages
using OpenTelemetry;
using OpenTelemetry.Resources;
using OpenTelemetry.Trace;
using OpenTelemetry.Exporter; -
Set the following environment variables
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINTwith value “http://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4318”OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOLwith value “http/protobuf”OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTESwith value “application=<APPLICATION_NAME>”OTEL_SERVICE_NAMEwith value “<SERVICE_NAME>”
-
Build the application and run it.
.NET Application Running in Linux / MacOS (.NET Core)
-
Download the instrumentation package from the O11ysource and extract it to your favorite folder. This is the OTel home directory.
-
Install opentelemetry core files by running the bash script
install.sh. This will install it in the dist folder. -
Activate the auto instrumentation by running the following commands
chmod +x dist/instrument.sh
export OTEL_DOTNET_AUTO_HOME=dist
. dist/instrument.sh -
This sets the required environment variables to the current terminal session.
-
Set the following environment variables in the same terminal session
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINTwith value “http://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4318”OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOLwith value “http/protobuf”OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTESwith value “application=<APPLICATION_NAME>”OTEL_SERVICE_NAMEwith value “<SERVICE_NAME>”
-
In the same terminal session, run the .NET application.
Remove the instrumentation
-
Go to the OTel Home directory
-
Run the following commands
chmod +x remove_instrumentation.sh
. ./remove_instrumentation.sh -
This removes the instrumentation, and you can run the application as usual.
.NET Application Running on Container (.NET Core)
-
Modify the Dockerfile to include the following lines to enable opentelemetry auto instrumentation
# install OpenTelemetry .NET Automatic Instrumentation
ARG OTEL_VERSION=1.4.0
ADD https://github.com/open-telemetry/opentelemetry-dotnet-instrumentation/releases/download/v${OTEL_VERSION}/otel-dotnet-auto-install.sh otel-dotnet-auto-install.sh
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y curl
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y unzip && \
OTEL_DOTNET_AUTO_HOME="/otel-dotnet-auto" sh otel-dotnet-auto-install.sh -
Build the docker image
-
Create a file called
otel-dotnet.envwith the following content# enable OpenTelemetry .NET Automatic Instrumentation
CORECLR_ENABLE_PROFILING="1"
CORECLR_PROFILER='{918728DD-259F-4A6A-AC2B-B85E1B658318}'
CORECLR_PROFILER_PATH="/otel-dotnet-auto/linux-x64/OpenTelemetry.AutoInstrumentation.Native.so"
DOTNET_ADDITIONAL_DEPS="/otel-dotnet-auto/AdditionalDeps"
DOTNET_SHARED_STORE="/otel-dotnet-auto/store"
DOTNET_STARTUP_HOOKS="/otel-dotnet-auto/net/OpenTelemetry.AutoInstrumentation.StartupHook.dll"
OTEL_DOTNET_AUTO_HOME="/otel-dotnet-auto" -
Run the Docker image with the following environment variables and env file
-env-file ./otel-dotnet.env --env OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT="http://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4318" OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL="http/protobuf" OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES="application=<APPLICATION_NAME>" OTEL_SERVICE_NAME="<SERVICE_NAME>"
ASP.NET Application running in IIS (.NET Framework & .NET Core)
-
Download the instrumentation package (
dotnet_auto_instrumentation_offline_package.zip) from the O11ysource and extract it. -
Open Powershell in administrator mode. Go into the folder where the instrumentation packages are extracted.
-
Install open telemetry auto instrumentation by running the powershell script
OpenTelemetry.DotNet.Auto.psm1# Import the module
Import-Module ".\OpenTelemetry.DotNet.Auto.psm1"
# Install core files
Install-OpenTelemetryCore -InstallDir "C:\Program Files\OpenTelemetry .NET AutoInstrumentation" -LocalPath ".\opentelemetry-dotnet-instrumentation-windows.zip"By default, this is installed in the “C:\Program Files\OpenTelemetry .NET AutoInstrumentation” directory. You can install this in any folder by changing the “InstallDir” option
-
Run the command
Register-OpenTelemetryForIIS. This will restart the IIS.# Setup IIS instrumentation
Register-OpenTelemetryForIIS
Security warning
Run only scripts that you trust. While scripts from the internet can be useful, this script can potentially harm your computer. If
you trust this script, use the Unblock-File cmdlet to allow the script to run without this warning message. Do you want to run
D:\Dev\dotnet-instrumentation\madrid\instrumentation-package\dotnet\auto-instrumentation\pkg\otel\OpenTelemetry.DotNet.Auto.psm1?
[D] Do not run [R] Run once [S] Suspend [?] Help (default is "D"): R
Attempting stop...
Internet services successfully stopped
Attempting start...
Internet services successfully restarted -
Set the setting to the application.
-
For .NET Framework applications.
- Using IIS manager, open the “Application Settings” of your application

- Add the following application settings.
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINTwith value “http://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4318”OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOLwith value “http/protobuf”OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTESwith value “application=<APPLICATION_NAME>,host.name=<host_name>,host.ip=<host_ip>”OTEL_SERVICE_NAMEwith value “<SERVICE_NAME>”OTEL_METRICS_EXPORTERwith value “none”OTEL_DOTNET_AUTO_TRACES_WCFSERVICE_INSTRUMENTATION_ENABLEDwith value “false”
- You can also set these values in the
<appSettings>section in theWeb.configfile. An example is shown below.
- Using IIS manager, open the “Application Settings” of your application
-
For .NET Core applications.
- Add the following application settings under the
<environmentVariables>in<aspNetCore>section in web.config fileOTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINTwith value “http://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4318”OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOLwith value “http/protobuf”OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTESwith value “application=<APPLICATION_NAME>,host.name=<host_name>,host.ip=<host_ip>”OTEL_SERVICE_NAMEwith value “<SERVICE_NAME>”OTEL_METRICS_EXPORTERwith value “none”
Example:
<aspNetCore processPath="dotnet" arguments=".\WebApplication2.dll" stdoutLogEnabled="true" stdoutLogFile=".\logs\stdout" hostingModel="inprocess" >
<environmentVariables>
<environmentVariable name="OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT" value="http://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4318" />
<environmentVariable name="OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL" value="http/protobuf" />
<environmentVariable name="OTEL_METRICS_EXPORTER" value="none" />
<environmentVariable name="OTEL_SERVICE_NAME" value="<SERVICE_NAME>" />
<environmentVariable name="OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES" value="application=<APPLICATION_NAME>,host.name=<HOST_NAME>,host.ip=<HOST_IP>" />
</environmentVariables>
</aspNetCore> - Add the following application settings under the
-
-
Restart IIS
Enable / Disable Instrumentation per Application Pool (.NET Framework only)
By default, all the applications are instrumented. But you can disable instrumentation per application pool.
# Import the module
Import-Module ".\OpenTelemetry.DotNet.Auto.psm1"
# Disable the instrumentation for the app pool
Disable-OpenTelemetryForIISAppPool -AppPoolName <App_Pool_Name>
# Restart Application Pool
Restart-WebAppPool -Name "MyAppPool"
To enable the instrumentation for the Application Pool, you can use the below command
# Import the module
Import-Module ".\OpenTelemetry.DotNet.Auto.psm1"
# Disable the instrumentation for the app pool
Enable-OpenTelemetryForIISAppPool -AppPoolName <App_Pool_Name>
# Restart Application Pool
Restart-WebAppPool -Name "MyAppPool"
Remove Instrumentation
- Run the following commands to remove the instrumentation.
# Import the module
Import-Module ".\OpenTelemetry.DotNet.Auto.psm1"
Unregister-OpenTelemetryForIIS
Uninstall-OpenTelemetryCore
.NET Application running as exe in Terminal
-
Download the instrumentation package (
dotnet_auto_instrumentation_offline_package.zip) from O11ysources and extract it. -
Open Powershell in administrator mode. Go into the folder where the instrumentation packages are extracted.
-
Install open telemetry auto instrumentation by running the powershell script
OpenTelemetry.DotNet.Auto.psm1# Import the module
Import-Module ".\OpenTelemetry.DotNet.Auto.psm1"
# Install core files
Install-OpenTelemetryCore -InstallDir "C:\Program Files\OpenTelemetry .NET AutoInstrumentation" -LocalPath ".\opentelemetry-dotnet-instrumentation-windows.zip"By default, this is installed in the “C:\Program Files\OpenTelemetry .NET AutoInstrumentation” directory. You can install this any folder by changing the “InstallDir” option
-
Run the command
Register-OpenTelemetryForCurrentSessionRegister-OpenTelemetryForCurrentSession -OTelServiceName "<service name>" -
Set the following environment variables
# Set environment variables for OpenTelemetry
$env:OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT = "http://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4318"
$env:OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL = "http/protobuf"
$env:OTEL_METRICS_EXPORTER = "none"
$env:OTEL_SERVICE_NAME = "<SERVICE_NAME>"
$env:OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES = "application=<APPLICATION_NAME>,host.name=<HOST_NAME>,host.ip=<HOST_IP>" -
Run the application exe
Uninstall Open telemetry for exe
- Install open telemetry auto instrumentation by running the powershell script
OpenTelemetry.DotNet.Auto.psm1# Import the module
Import-Module ".\OpenTelemetry.DotNet.Auto.psm1"
Unregister-OpenTelemetryForCurrentSession
Uninstall-OpenTelemetryCore
Remove-Item -Path env:OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT
Remove-Item -Path env:OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL
Remove-Item -Path env:OTEL_METRICS_EXPORTER
Remove-Item -Path env:OTEL_SERVICE_NAME
Remove-Item -Path env:OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES
.NET Application running as exe in Task Scheduler
-
Download the instrumentation package (
dotnet_auto_instrumentation_offline_package.zip) from O11ysources and extract it. -
Open Powershell in administrator mode. Go into the folder where the instrumentation packages are extracted.
-
Install open telemetry auto instrumentation by running the powershell script
OpenTelemetry.DotNet.Auto.psm1# Import the module
Import-Module ".\OpenTelemetry.DotNet.Auto.psm1"
# Install core files
Install-OpenTelemetryCore -InstallDir "C:\Program Files\OpenTelemetry .NET AutoInstrumentation" -LocalPath ".\opentelemetry-dotnet-instrumentation-windows.zip"By default, this is installed in the “C:\Program Files\OpenTelemetry .NET AutoInstrumentation” directory. You can install this in any folder by changing the “InstallDir” option
-
Create a wrapper PowerShell script to wrap your exe
# Configure the Service Name
$OTelServiceName = "SERVICE_NAME"
# Configure the OTel installation path
$installDir = "C:\Program Files\OpenTelemetry .NET AutoInstrumentation"
# Configure your exe path
$exePath = "C:\MyDotNetApp.exe"
# Configure the resource attributes
$applicationName = "APPLICATION_NAME"
$hostName = "HOST_NAME"
$hostIp = "HOST_IP"
# Configure OpenTelemetry Exporter settings
$otelExporterOtlpEndpoint = "http://<vuSmartMaps Server IP>:4318"
$otelExporterOtlpProtocol = "http/protobuf"
$otelMetricsExporter = "none"
$otelResourceAttributes = "application=$applicationName,host.name=$hostName,host.ip=$hostIp"
# Create the environment variables directly in the script
$varsTable = @{
"OTEL_SERVICE_NAME" = $OTelServiceName
"OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES" = $otelResourceAttributes
"OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT" = $otelExporterOtlpEndpoint
"OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL" = $otelExporterOtlpProtocol
"OTEL_METRICS_EXPORTER" = $otelMetricsExporter
"COR_ENABLE_PROFILING" = "1"
"COR_PROFILER" = "{918728DD-259F-4A6A-AC2B-B85E1B658318}"
"COR_PROFILER_PATH_64" = "$installDir\win-x64\OpenTelemetry.AutoInstrumentation.Native.dll"
"COR_PROFILER_PATH_32" = "$installDir\win-x86\OpenTelemetry.AutoInstrumentation.Native.dll"
"CORECLR_ENABLE_PROFILING" = "1"
"CORECLR_PROFILER" = "{918728DD-259F-4A6A-AC2B-B85E1B658318}"
"CORECLR_PROFILER_PATH_32" = "$installDir\win-x86\OpenTelemetry.AutoInstrumentation.Native.dll"
"CORECLR_PROFILER_PATH_64" = "$installDir\win-x64\OpenTelemetry.AutoInstrumentation.Native.dll"
"ASPNETCORE_HOSTINGSTARTUPASSEMBLIES" = "OpenTelemetry.AutoInstrumentation.AspNetCoreBootstrapper"
"DOTNET_ADDITIONAL_DEPS" = "$installDir\AdditionalDeps"
"DOTNET_SHARED_STORE" = "$installDir\store"
"DOTNET_STARTUP_HOOKS" = "$installDir\net\OpenTelemetry.AutoInstrumentation.StartupHook.dll"
"OTEL_DOTNET_AUTO_HOME" = $installDir
}
# Set environment variables for the current session
foreach ($var in $varsTable.Keys) {
[System.Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable($var, $varsTable[$var], [System.EnvironmentVariableTarget]::Process)
}
# Run the .NET application
& $exePathConfigure the following to match your environment
- Service Name - Configure the correct SERVICE_NAME
- Install Dir - Configure the correct install directory of OTel
- Exe Path - Make sure you mention the correct path of the exe
- Application Name - Provide the correct application name
- Host Name - You can provide the host name. If you dont need host name then remove it from
$otelResourceAttributes = "application=$applicationName,host.name=$hostName,host.ip=$hostIp" - Host IP - You can provide the host ip. If you dont need host name then remove it from
$otelResourceAttributes = "application=$applicationName,host.name=$hostName,host.ip=$hostIp" - OTel Exporter Otlp Endpoint - Change this to the OTel collector endpoint
-
Modify your task
- Open Task Scheduler and find your task.
- Right-click the task and select Properties.
- Go to the Actions tab and click Edit.
- In the Action section, choose Start a program.
- For the Program/script, enter the full path to
powershell.exe. The path is typically “C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe” - In the Add arguments (optional) field, enter the following
-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File "<full path of the wrapper powershell script you created>"
Example:
-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File "C:\Myne\instrument-exe\MyDotNetApp\MyApp.ps1"
Uninstall Open telemetry for exe running in Task Scheduler
- Uninstall open telemetry auto instrumentation by running the powershell script
OpenTelemetry.DotNet.Auto.psm1# Import the module
Import-Module ".\OpenTelemetry.DotNet.Auto.psm1"
Uninstall-OpenTelemetryCore - Modify your task
- Open Task Scheduler and find your task.
- Right-click the task and select Properties.
- Go to the Actions tab and click Edit.
- In the Action section, choose Start a program.
- For the Program/script, enter your exe path and save.
Configuration
Capture HTTP Headers
In some applications, key transaction identifiers are passed as HTTP headers to the APIs. To capture these headers, additional instrumentation configurations are required. Below are the steps and examples for capturing HTTP headers for both HTTP servers and clients.
Capture HTTP Request Header for ASP.NET Core
To capture the request headers of ASP.NET Core, use the following configuration along with other instrumentation configurations mentioned in the previous sections.
OTEL_DOTNET_AUTO_TRACES_ASPNETCORE_INSTRUMENTATION_CAPTURE_REQUEST_HEADERS
You can configure one or more headers to be captured. If capturing multiple headers, separate them with commas. Based on the environment, add this additional configuration. For example
OTEL_DOTNET_AUTO_TRACES_ASPNETCORE_INSTRUMENTATION_CAPTURE_REQUEST_HEADERS=client_id,applicationid
Capture HTTP Response Header for ASP.NET Core
To capture the response headers of ASP.NET Core, use the following configuration along with other instrumentation configurations mentioned in the previous sections.
OTEL_DOTNET_AUTO_TRACES_ASPNETCORE_INSTRUMENTATION_CAPTURE_RESPONSE_HEADERS
You can configure one or more headers to be captured. If capturing multiple headers, separate them with commas. Based on the environment, add this additional configuration. For example
OTEL_DOTNET_AUTO_TRACES_ASPNETCORE_INSTRUMENTATION_CAPTURE_REQUEST_HEADERS=respo_code,resp_status
Capture HTTP Request Header for ASP.NET
To capture the request headers of ASP.NET, use the following configuration along with other instrumentation configurations mentioned in the previous sections.
OTEL_DOTNET_AUTO_TRACES_ASPNET_INSTRUMENTATION_CAPTURE_REQUEST_HEADERS
You can configure one or more headers to be captured. If capturing multiple headers, separate them with commas. Based on the environment, add this additional configuration. For example
OTEL_DOTNET_AUTO_TRACES_ASPNET_INSTRUMENTATION_CAPTURE_REQUEST_HEADERS=client_id,applicationid
Capture HTTP Response Header for ASP.NET
To capture the response headers of ASP.NE, use the following configuration along with other instrumentation configurations mentioned in the previous sections.
OTEL_DOTNET_AUTO_TRACES_ASPNET_INSTRUMENTATION_CAPTURE_RESPONSE_HEADERS
You can configure one or more headers to be captured. If capturing multiple headers, separate them with commas. Based on the environment, add this additional configuration. For example
OTEL_DOTNET_AUTO_TRACES_ASPNET_INSTRUMENTATION_CAPTURE_RESPONSE_HEADERS=respo_code,resp_status
Instrumentation Process
Linux
This option is suitable if you are running your application on the host machine directly as a process by running the application binary.
- Download the instrumentation binary from O11ySources.
- Run your application as usual.
- Add the following environment variables: (To see the list of all available configurations see here)
# Use grpc protocol while exporting traces
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL=grpc
# endpoint to which the spans are to be exported
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT=http://collector:4317
# path where the application binary is placed in the system
OTEL_GO_AUTO_TARGET_EXE=/go/payment_switch
# whether to include and parse sql statements for the database calls
OTEL_GO_AUTO_INCLUDE_DB_STATEMENT=true
# Sets whether to parse the SQL statement for trace data, setting db.operation.name. Only valid if OTEL_GO_AUTO_INCLUDE_DB_STATEMENT is also set.
OTEL_GO_AUTO_PARSE_DB_STATEMENT=true
# name of the application
OTEL_SERVICE_NAME=payment_switch
OTEL_PROPAGATORS=tracecontext,baggage - Finally, start the instrumentation binary:
sudo ./otel-go-instrumentation
We should now be able to see the spans being generated and being pushed to the collector configured. If the instrumentation binary is run before the application is started the instrumentation binary will wait for the application on start up.
Docker/Docker-Compose
Although not heavily used in production setups, docker-compose is one of the ways to run and orchestrate multi-layered applications. To instrument them, we shall run the instrumentation binary as a side car container to them.
- Add the below service to the
docker-compose.ymlfile where you defined the application:go-auto:
depends_on:
- payment_switch
image: otel/autoinstrumentation-go
privileged: true
pid: "host"
volumes:
- /proc:/host/proc
environment:
- OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL=grpc
- OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT=http://collector:4317
- OTEL_GO_AUTO_TARGET_EXE=/go/payment_switch
- OTEL_GO_AUTO_INCLUDE_DB_STATEMENT=true
- OTEL_GO_AUTO_PARSE_DB_STATEMENT=true
- OTEL_SERVICE_NAME=payment_switch
payment_switch:
pid: "host"
volumes:
- /proc:/host/proc
...- Save the file and run
docker-compose up
notepid: “container:payment_switch”allows the instrumentation binary to access and interact with the processes running in thepayment_switchcontainer. And this is how the instrumentation binary gets access to the running application. - Save the file and run
Instrumentation Process
-
Download the Opentelemetry Operator helm chart from O11ysources and install it
helm install opentelemetry-operator opentelemetry-operator-0.71.0.tgz \
--namespace opentelemetry-operator-system \
--create-namespace \
--set "manager.collectorImage.repository=otel/opentelemetry-collector-k8s" \
--set admissionWebhooks.certManager.enabled=false \
--set admissionWebhooks.autoGenerateCert.enabled=true -
Download the vuTraces auto instrumentation helm chart from O11ysources and install it
helm install vutraces-auto-instrumentation vutraces-auto-instrumentation-1.0.0.tgz \
--namespace opentelemetry-operator-system \
--create-namespace \
--set vutracesexporter.endpoint="http://<vuSmartMaps_server:4317" -
Add the following annotation to your deployments.
-
Java workloads
annotations:
instrumentation.opentelemetry.io/inject-java: "opentelemetry-operator-system/vutraces-auto-instrumentation" -
.NET workloads
annotations:
instrumentation.opentelemetry.io/inject-dotnet: "opentelemetry-operator-system/vutraces-auto-instrumentation" -
Go workloads
annotations:
instrumentation.opentelemetry.io/inject-go: "opentelemetry-operator-system/vutraces-auto-instrumentation"If there are multiple containers exists in the pod, then add the below annotation too
annotations:
instrumentation.opentelemetry.io/container-names: <name of the application container> -
Python workloads
annotations:
instrumentation.opentelemetry.io/inject-python: "opentelemetry-operator-system/vutraces-auto-instrumentation"By default, the annotation defined above works for applications running under glibc based python images. If you are using a musl based python image for your application, add the below annotation as well.
annotations:
instrumentation.opentelemetry.io/otel-python-platform: "musl" -
Node.js Workloads
annotations:
instrumentation.opentelemetry.io/inject-nodejs: "opentelemetry-operator-system/vutraces-auto-instrumentation" -
If you have a limited number of deployments in your cluster, modify your application helm charts or k8s manifests. In the deployment add the annotation in
spec -> template -> metadata -
If you have many deployments and it is not possible to manually update them then do some automation. One such automation script is available here. Please use this as a reference and create an automation script that works for your environment.
-
The annotations can be also added at the namespace
-
-
If there are multiple containers exists in the pod, then add the below annotation too
annotations:
instrumentation.opentelemetry.io/container-names: <name of the application container> -
Add the following environment variable in the deployment to set the application name.
name: OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES
value: "application=<app_name>" -
Add the following environment variable in the deployment to configure the HTTP Headers to be captured.
- Java Workloads
-
Capture HTTP Request Header for HTTP Server
name: OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_HTTP_SERVER_CAPTURE_REQUEST_HEADERS
value: "Header1,Header2" -
Capture HTTP Response Header for HTTP Server
name: OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_HTTP_SERVER_CAPTURE_RESPONSE_HEADERS
value: "Header3,Header4" -
Capture HTTP Request Header for HTTP Client
name: OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_HTTP_CLIENT_CAPTURE_REQUEST_HEADERS
value: "Header5,Header6" -
Capture HTTP Response Header for HTTP Client
name: OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_HTTP_SERVER_CAPTURE_REQUEST_HEADERS
value: "Header7,Header8"
-
- .NET Workloads
-
Capture HTTP Request Header for ASP.NET Core
name: OTEL_DOTNET_AUTO_TRACES_ASPNETCORE_INSTRUMENTATION_CAPTURE_REQUEST_HEADER
value: "Header1,Header2" -
Capture HTTP Response Header for ASP.NET Core
name: OTEL_DOTNET_AUTO_TRACES_ASPNETCORE_INSTRUMENTATION_CAPTURE_RESPONSE_HEADERS
value: "Header3,Header4" -
Capture HTTP Request Header for ASP.NET
name: OTEL_DOTNET_AUTO_TRACES_ASPNET_INSTRUMENTATION_CAPTURE_REQUEST_HEADERS
value: "Header5,Header6" -
Capture HTTP Response Header for ASP.NET
name: OTEL_DOTNET_AUTO_TRACES_ASPNET_INSTRUMENTATION_CAPTURE_RESPONSE_HEADERS
value: "Header7,Header8"
-
- Java Workloads
Instrumentation Process
Instrumentation for Node.js requires the installation of a couple of opentelemetry libraries as dependencies in the application regardless of the environment in which they are run. Along with this we can configure the instrumentation through environment variables. We shall explain the steps to achieve them and various options available below:
Installing Dependencies
The following two libraries are required to be installed as dependencies by using npm install –save or adding them to the `package.json` directly and running npm install
npm install --save @opentelemetry/api
npm install --save @opentelemetry/auto-instrumentations-node
--save options saves the installed dependencies to package.json file automatically. After running the command you should see this change in package.json.
"dependencies": {
"@opentelemetry/api": "^1.9.0",
"@opentelemetry/auto-instrumentations-node": "^0.57.1",
…
}
If the environment doesn’t have access to the internet to install the packages, use the provided tar files of the packages and place them in the same directory as package.json. Once done edit the package.json to include the below two lines in the dependencies section and run npm install --offline.
"dependencies": {
"@opentelemetry/api": "file:./api-1.9.0.tgz",
"@opentelemetry/auto-instrumentations-node": "file:./auto-instrumentations-node-0.59.0.tgz",
...
}
opentelemetry/api
This package provides everything needed to interact with the OpenTelemetry API, including all TypeScript interfaces, enums, and no-op implementations. It is intended for use both on the server and in the browser.
The methods in this package perform no operations by default. This means they can be safely called by a library or end-user application whether there is an SDK registered or not.
opentelemetry/auto-instrumentations-node
This module provides a way to auto instrument any Node application to capture telemetry from a number of popular libraries and frameworks. You can export the telemetry data in a variety of formats. Exporters, samplers, and more can be configured via environment variables. The net result is the ability to gather telemetry data from a Node application without any code changes. The list of supported libraries can be found here.
Configuring the Instrumentation
All configurations are done through environment variables as with other languages. Below are some of the mandatory and important envs to be added:
OTEL_TRACES_EXPORTER
The type of exporter to use for sending the generated traces. Possible values include otlp, console and zipkin. Since we use the OTEL collector to capture the traces, the value must be set to otlp.
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_TRACES_ENDPOINT
The endpoint where the OTEL collector is running. For example: http://localhost:4317, http://otel-collector:4318 etc.. As a convention usually port 4317 is configured on grpc protocol and 4318 for http protocol in the OTEL collector. Select the port accordingly. In most cases, unless specified, the default port is 4317 with grpc.
OTEL_SERVICE_NAME
The name of the service being instrumented. This value will be used and saved in the generated traces under the field resource_attributes_service_name.
OTEL_NODE_ENABLED_INSTRUMENTATIONS
By default all the supported modules installed in the application will generate traces. We can configure this to allow only a certain number of modules to generate traces using this environment variable. Add the names of the modules to be instrumented as comma separated values. For example: OTEL_NODE_ENABLED_INSTRUMENTATIONS=http,express,pg.
OTEL_TRACES_EXPORTER
In cases where we need to disable instrumentation for a set of libraries, we can use the environment variable. For ex: OTEL_NODE_DISABLED_INSTRUMENTATIONS="express,pg". This will not generate traces of http server calls handled by express and db calls made by pg respectively.
Running the Application
After the above steps are completed, run the application using the below command:
node --require @opentelemetry/auto-instrumentations-node/register app.js
where app.js is assumed to be the entrypoint for the application, but change this accordingly for your application. Note that we require the register module from the auto-instrumentations-node library before the application startup.
Alternatively, we can use the NODE_OPTION environment variable to require the register before the application startup.
export NODE_OPTIONS="--require @opentelemetry/auto-instrumentations-node/register"
node app.js
Instrumentation Process
Instrumentation for Python requires the installation of a couple of opentelemetry libraries as dependencies in the application regardless of the environment in which they are run. Along with this we can configure the instrumentation through environment variables. We shall explain the steps to achieve them and various options available below:
Installing Dependencies
The following two libraries are required to be installed as dependencies either by using the .whl file provided or directly from the pip repository if connected to the internet.
pip install opentelemetry-distro
# pip install opentelemetry_distro-0.54b0-py3-none-any.whl
Additional optional packages (based on your exporters and protocols):
pip install opentelemetry-exporter-otlp
# pip install opentelemetry_exporter_otlp-1.33.0-py3-none-any.whl
pip install opentelemetry-instrumentation
# pip install opentelemetry_instrumentation-0.54b0-py3-none-any.whl
Package Details
- opentelemetry-distro: Sets up OpenTelemetry with sensible defaults and zero-code instrumentation.
- opentelemetry-exporter-otlp: Allows exporting telemetry data to the OpenTelemetry Collector.
- opentelemetry-instrumentation: Provides auto-instrumentation for various popular Python libraries. Here is the complete list.
Configuring the Instrumentation
All configurations are done through environment variables as with other languages. Below are some of the mandatory and important envs to be added:
OTEL_TRACES_EXPORTER
The type of exporter to use for sending the generated traces. Possible values include otlp, console and zipkin. Since we use the OTEL collector to capture the traces, the value must be set to otlp.
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_TRACES_ENDPOINT
The endpoint where the OTEL collector is running. For example: http://localhost:4317, http://otel-collector:4318 etc.. As a convention usually port 4317 is configured on grpc protocol and 4318 for http protocol in the OTEL collector. Select the port accordingly. In most cases, unless specified, the default port is 4317 with grpc.
OTEL_SERVICE_NAME
The name of the service being instrumented. This value will be used and saved in the generated traces under the field resource_attributes_service_name.
OTEL_PYTHON_DISABLED_INSTRUMENTATIONS
Comma-separated list of libraries to disable auto-instrumentation. By default all libraries supported and available in the environment will be instrumented.
Running the Application
After the above steps are completed, run the application using the below command:
opentelemetry-instrument python app.py
where app.py is assumed to be the entrypoint for the application, but change this accordingly for your application. For gunicorn-based apps:
opentelemetry-instrument gunicorn app:app
Instrumentation Process
Prebuilt packages of the module are available for easy installation. Follow these steps to install NGINX Open Source with the OTel module. See list of compatible operating systems.
Adding Package Repositories and Installing NGINX Open Source
Follow the official NGINX Open Source installation steps to set up package repositories for your specific operating system and install NGINX.
Installing Nginx on Ubuntu
Install the prerequisites:
sudo apt install curl gnupg2 ca-certificates lsb-release ubuntu-keyring
Import an official nginx signing key so apt could verify the packages authenticity. Fetch the key:
curl https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key | gpg --dearmor \
| sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg >/dev/null
Verify that the downloaded file contains the proper key:
gpg --dry-run --quiet --no-keyring --import --import-options import-show /usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg
The output should contain the full fingerprint 573BFD6B3D8FBC641079A6ABABF5BD827BD9BF62 as follows:
pub rsa2048 2011-08-19 [SC] [expires: 2027-05-24]
573BFD6B3D8FBC641079A6ABABF5BD827BD9BF62
uid nginx signing key <[email protected]>
Note that the output can contain other keys used to sign the packages.
To set up the apt repository for stable nginx packages, run the following command:
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg] \
http://nginx.org/packages/ubuntu `lsb_release -cs` nginx" \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nginx.list
If you would like to use mainline nginx packages, run the following command instead:
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg] \
http://nginx.org/packages/mainline/ubuntu `lsb_release -cs` nginx" \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nginx.list
Set up repository pinning to prefer our packages over distribution-provided ones:
echo -e "Package: *\nPin: origin nginx.org\nPin: release o=nginx\nPin-Priority: 900\n" \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/preferences.d/99nginx
To install nginx, run the following commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nginx
Installing the OTel Module from Packages
sudo apt install nginx-module-otel
Enabling the OTel Module
Module configurations can be found here.
Following the installation steps above will install the module into /etc/nginx/modules by default. Load the module by adding the following line to the top of the main NGINX configuration file, located at /etc/nginx/nginx.conf.
Example Configuration:
load_module modules/ngx_otel_module.so;
http {
otel_exporter {
endpoint 172.16.115.75:4317;
interval 5s;
batch_size 512;
batch_count 4;
}
otel_trace on;
otel_service_name vubank_nginx;
}
user www-data;
load_module modules/ngx_otel_module.so;
worker_processes auto;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
include /etc/nginx/modules-enabled/*.conf;
Below is the sample nginx.conf used for vuBank where OTEL module is enabled
user www-data;
load_module modules/ngx_otel_module.so;
worker_processes auto;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
include /etc/nginx/modules-enabled/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections 768;
# multi_accept on;
}
http {
otel_exporter {
endpoint 172.16.115.75:4317;
interval 5s;
batch_size 512;
batch_count 4;
}
otel_trace on;
otel_service_name vubank_nginx;
##
# Basic Settings
##
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
# server_tokens off;
# server_names_hash_bucket_size 64;
# server_name_in_redirect off;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
##
# SSL Settings
##
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3; # Dropping SSLv3, ref: POODLE
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
##
# Logging Settings
##
#log_format access_format 'time: $time_iso8601,' ' bytes_sent: $bytes_sent,' ' connection_time: $connection_time,' ' nginx_host: $host,' ' pid: $pid,' ' proxy_host: $proxy_host,' ' proxy_port: $proxy_port,' ' realip_remote_addr: $realip_remote_addr,' ' realip_remote_port: $realip_remote_port,' ' remote_addr: $remote_addr,' ' remote_port: $remote_port,' ' request: $request,' ' request_filename: $request_filename,' ' request_method: $request_method,' ' request_time: $request_time,' ' request_uri: $request_uri,' ' server_addr: $server_addr,' ' server_name: $server_name,' ' server_port: $server_port,' ' server_protocol: $server_protocol,' ' ssl_client_verify: $ssl_client_verify,' ' ssl_protocol: $ssl_protocol,' ' ssl_server_name: $ssl_server_name,' ' ssl_session_id: $ssl_session_id,' ' ssl_session_reused: $ssl_session_reused,' ' status: $status,' ' upstream_addr: $upstream_addr,' ' upstream_bytes_received: $upstream_bytes_received,' ' upstream_bytes_sent: $upstream_bytes_sent,' ' upstream_cache_status: $upstream_cache_status,' ' upstream_connect_time: $upstream_connect_time,' ' upstream_response_time: $upstream_response_time';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
##
# Gzip Settings
##
gzip on;
# gzip_vary on;
# gzip_proxied any;
# gzip_comp_level 6;
# gzip_buffers 16 8k;
# gzip_http_version 1.1;
# gzip_types text/plain text/css application/json application/javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript;
##
# Virtual Host Configs
##
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*;
upstream backend {
#server 172.16.112.18:80;
server localhost:8085;
# Add more backend servers here as needed
}
upstream rum-backend {
#server 172.16.124.188:4319;
server 172.16.120.225:4319;
}
server {
listen 164.52.200.135:80;
#server_name vubank2.vunetsystems.com;
location /rum/ {
proxy_pass http://rum-backend/;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_buffering off;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin *;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Methods "POST, OPTIONS";
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Headers "Content-Type, Authorization";
if ($request_method = 'OPTIONS') {
return 204;
}
error_log /var/log/nginx/rum_debug.log debug;
}
location /api/auth/login {
#deny 164.52.200.135;
proxy_pass http://backend/auth/login;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
location /api/accounts {
#deny 164.52.200.135;
proxy_pass http://backend/accounts;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
location /api/payees {
#deny 164.52.200.135;
proxy_pass http://backend/payees;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend/;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
#return 404;
}
location /server_status {
#deny 164.52.200.135;
stub_status on;
access_log on;
allow all;
# deny all;
# proxy_pass http://backend;
}
}
}
Restart the nginx for the changes to take effect
sudo service nginx restart
Generating Load
To generate load you can login to vuBank. This would hit the Nginx webserver.
Verfiy the OTEL Data
To verify if the OTEL data from Nginx , login to to kafka and check the traces-input topic.
kubectl exec -it kafka-cluster-cp-kafka-0 -nvsmaps bash
[appuser@kafka-cluster-cp-kafka-0 ~]$ kafka-console-consumer --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic input-metrics | grep nginx
Could not start Jolokia agent: java.net.BindException: Address already in use
{"application":"vubank_nginx","call_count":1,"duration_bucket_counts":[0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],"duration_explicit_bounds":[2,4,6,8,10,50,100,200,500,800,1000,1400,2000,5000,10000,15000],"duration_sum":3,"environment":"","error_count":0,"host_ip":"","host_name":"","http_status_code":200,"service":"vubank_nginx","service_name":"vubank_nginx","span_kind":"SPAN_KIND_SERVER","span_name":"/","start_time":"2025-03-25T01:46:05.358434104Z","status_code":"STATUS_CODE_UNSET","timestamp":"2025-03-25T05:47:05.359298852Z"}
{"application":"vubank_nginx","call_count":1,"duration_bucket_counts":[0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],"duration_explicit_bounds":[2,4,6,8,10,50,100,200,500,800,1000,1400,2000,5000,10000,15000],"duration_sum":3,"environment":"","error_count":0,"host_ip":"","host_name":"","http_status_code":200,"service":"vubank_nginx","service_name":"vubank_nginx","span_kind":"SPAN_KIND_SERVER","span_name":"/","start_time":"2025-03-25T01:46:05.358434104Z","status_code":"STATUS_CODE_UNSET","timestamp":"2025-03-25T05:47:35.359504329Z"}
unet@e2e-72-51:~$ kubectl exec -it kafka-cluster-cp-kafka-0 -nvsmaps bash
kubectl exec [POD] [COMMAND] is DEPRECATED and will be removed in a future version. Use kubectl exec [POD] -- [COMMAND] instead.
[appuser@kafka-cluster-cp-kafka-0 ~]$ kafka-console-consumer --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic traces-input | grep vubank_nginx
Could not start Jolokia agent: java.net.BindException: Address already in use
{"is_root_span":true,"resource_attributes_service_name":"vubank_nginx","spanId":"f38f18b1c6a207f2","span_attributes_http_flavor":"1.1","span_attributes_http_method":"GET","span_attributes_http_request_content_length":0,"span_attributes_http_response_content_length":0,"span_attributes_http_route":"/","span_attributes_http_scheme":"http","span_attributes_http_status_code":304,"span_attributes_http_target":"/","span_attributes_http_user_agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/131.0.0.0 Safari/537.36","span_attributes_instrumentation_library_name":"nginx","span_attributes_net_host_name":"164.52.200.135","span_attributes_net_sock_peer_addr":"103.139.158.118","span_attributes_net_sock_peer_port":22179,"span_attributes_service":"vubank_nginx","span_attributes_site":"default","span_attributes_transaction":"GET /","span_durationNano":2000000,"span_end_time":"2025-03-25T05:55:40.634Z","span_kind":"SPAN_KIND_SERVER","span_name":"/","span_parentSpanId":"","span_start_time":"2025-03-25T05:55:40.632Z","status_code":0,"timestamp":"2025-03-25T05:55:40.634Z","traceId":"bfec18c7823a734738fc169b537f1f7d"}
In the Otel data we should be able to see resouce_attributes_service_name coming with vubank_nginx.
