LDAP Integration
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) integration allows organizations to centralize authentication and user management by leveraging an external directory service. LDAP integration in vuSmartMaps supports multiple scenarios, ensuring flexibility in user and role management.
- Centralized authentication using existing user credentials.
- Seamless user access management across multiple applications.
- Enhanced security with minimal administrative overhead.
LDAP Integration Scenarios
With vuSmartMaps, users can integrate LDAP in different ways depending on their organization's needs. Below are the three primary scenarios that administrators may encounter when integrating LDAP.
Scenario 1: No LDAP Integration (Local User Management)
This scenario is designed for organizations that prefer to manage their authentication and authorization processes entirely within vuSmartMaps, without integrating LDAP. All users and roles are created and maintained locally, ensuring complete control over access management. It is ideal for organizations that either do not have an LDAP setup or prefer to keep user and role administration independent of an external directory service.
Use Case
- Organizations that do not have an LDAP server or prefer managing authentication and authorization locally within vuSmartMaps.
- Useful for small teams that need simple access control.
- Suitable for businesses that do not require external user authentication and want to maintain full control over user access within the application.
Implementation Workflow
- Administrators manually create and manage users and roles in the User Management Module.
- No synchronization or dependency on external LDAP servers.
- User credentials and permissions are stored and managed entirely within vuSmartMaps.
- Navigate to the User Management Module to create and assign users & roles manually.
- Manage permissions for these locally created roles within User Management and map users to the relevant roles.
- Maintain user lifecycle, including onboarding, offboarding, and permission updates, within vuSmartMaps.
Scenario 2: Users Pulled from LDAP, Roles Assigned by vuSmartMaps
This scenario is suitable for organizations that rely on LDAP for user authentication but need flexibility in role management. While users are imported from LDAP, roles and their associated permissions are created and managed within vuSmartMaps. This approach allows administrators to have local control over authorization policies while leveraging LDAP authentication for a seamless login experience.
Use Case
- Organizations that authenticate users via LDAP but need flexibility in assigning roles.
- Suitable when LDAP is used for authentication only, while access control policies vary within vuSmartMaps.
- Ideal for cases where role assignments change frequently, or LDAP does not store roles.
- Provides a hybrid approach where authentication remains centralized, but authorization is managed locally.
Implementation Workflow
- Users are synchronized by integrating LDAP with vuSmartMaps, but role management is handled within vuSmartMaps.
- Administrators can create roles locally in User Management, define their permissions, and map imported LDAP users to these roles.
- Users log in with their LDAP credentials, but their access rights are determined by local role assignments in vuSmartMaps.
- Any updates to user credentials (e.g., password changes) are handled in LDAP, while role changes occur within vuSmartMaps.
- Regularly review and update local role assignments to reflect organizational changes.
- If required explicitly, users that are not part of LDAP can still be created locally, as defined in Scenario 1.
Scenario 3: Users and Roles Pulled from LDAP
This scenario is ideal for organizations that want to fully integrate LDAP for authentication and authorization. In this setup, users and roles are imported directly from LDAP, ensuring that all role assignments are consistent with the organization's centralized identity management policies. Administrators only need to manage permissions in vuSmartMaps, while user-to-role mappings are enforced by LDAP.
Use Case
- Organizations that centrally manage user roles within LDAP and want to enforce strict role mapping.
- Enterprises where role-based access control (RBAC) is already established in LDAP and needs to be mirrored in vuSmartMaps.
- Suitable for large businesses with well-defined organizational hierarchies and strict access policies.
Implementation Workflow
- Users get imported with LDAP integration.
- To pull roles, you need to create a mapper of type Group LDAP Mapper. This pulls the groups from LDAP, which then become roles in vuSmartMaps. With this, user-to-role mapping is pulled directly from the customer's LDAP environment.
- Manage role-based permissions within vuSmartMaps to define access levels for different roles.
- Ensure that periodic synchronization is configured correctly to reflect updates from LDAP in vuSmartMaps.
- If required explicitly, users and roles that are not part of LDAP can still be created locally, as defined in Scenario 1.
Choosing the Right Scenario:
vuSmartMaps supports all three scenarios, offering flexibility to the end-user as per their use case or requirement. Choose the scenario that fits best and proceed with integration. Your organization's environment may fit into any one of these three scenarios, but some cases may require a mix-and-match approach. For example:
- You may import all users and roles from LDAP but also need to create additional users and roles locally.
- You may import users and roles from LDAP but want to define additional role mappings locally for more control.
- Some roles may be imported from LDAP, but you may want to override permissions locally for certain users.
Role and User Mapping Permissions in LDAP Integration
From release NG-2.14 onwards, the restriction on editing LDAP users and roles mapping has been removed, enabling seamless integration of LDAP with vuSmartMaps. The following table outlines the possible actions regarding role-to-user mappings and whether they are allowed within vuSmartMaps:
| Action | Mapping | Allowed? |
|---|---|---|
| Add Mapping | LDAP Roles to LDAP Users | ✅ Allowed |
| Remove Mapping | LDAP Users from LDAP Roles | ❌ Not Allowed |
| Add Mapping | LDAP Roles to Local Users | ✅ Allowed |
| Remove Mapping | Local Users from LDAP Roles | ✅ Allowed |
| Add Mapping | Local Roles to LDAP Users | ✅ Allowed |
| Remove Mapping | LDAP Users from Local Roles | ✅ Allowed |
| Add Mapping | Local Roles to Local Users | ✅ Allowed |
| Remove Mapping | Local Users from Local Roles | ✅ Allowed |
Attempting to remove an LDAP role mapping from an LDAP user will result in the following error message: "Role Mapping configured in LDAP cannot be removed. Please use LDAP to delete the role mapping."
Summary of LDAP Integration Behavior
- LDAP Roles mapped to LDAP Users cannot be removed in vuSmartMaps.
- Local roles can be assigned or removed for both LDAP and Local users.
- Local users and roles can still be created separately without impacting LDAP.
- Administrators can manage permissions efficiently without modifying the organization's LDAP setup.
This setup ensures a flexible and seamless integration of LDAP with vuSmartMaps, allowing organizations to adapt authentication and authorization as per their security policies and operational needs.
Accessing User Federation
The User Federation module in vuSmartMaps allows access to external databases and directories, including LDAP and Active Directory.
- The User Federation page can be accessed from the platform left navigation menu by navigating to Platform Settings > User Federation.
- Upon entering the User Federation module, the landing page, when no provider is added, shows the message, “You don’t have any user federation configured. To configure one, click the ‘+ New Provider’ button.”
Read and write permissions to the Preferences module are needed to access the user federation module.
Adding a New LDAP Provider
- To add a new LDAP provider, click the + New Provider button and select LDAP.
- Provide the necessary details for adding an LDAP provider.
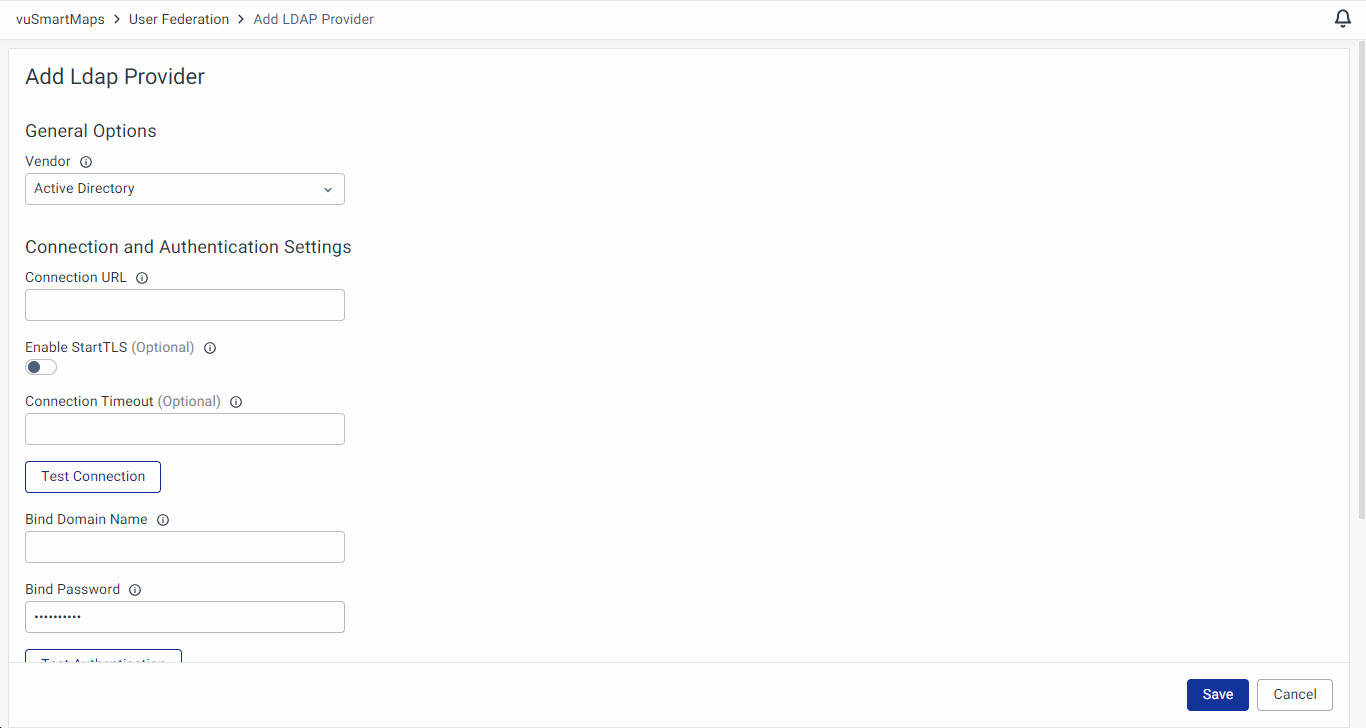
- General Options
- Vendor: Select LDAP Vendor (provider) – options include Active Directory, Red Hat Directory Server, Tivoli, Novell eDirectory, and Other.
- Connection and Authentication Settings:
- Connection URL: Connection URL to your LDAP Server.
- Enable StartTLS (Optional): Encrypts the connection to LDAP using StartTLS, which will disable connection pooling.
- Connection Timeout (Optional): LDAP connection timeout in milliseconds.
- Test Connection Button: Test if the connection is established.
- Bind Type: The Bind Type defines the authentication method used during the LDAP bind operation. It is used in most of the requests sent to the LDAP server. Currently, two options are available:
- None: This option uses anonymous LDAP authentication.
- Simple: This option uses bind credentials (LDAP admin credentials) and the bind password for authentication.
- Bind DN: Provide the Distinguished Name (DN) of the LDAP admin. IDP will use this DN to access the LDAP server.
- Bind Password: Password of the LDAP admin.
- Test Authentication Button: Test authentication with the server.
- LDAP Searching and Updating
- Users Domain Name: Specify the full DN of the LDAP tree where user data is located.
- Username LDAP Attribute: Define the LDAP attribute that is mapped as the IDP's username.
- User Object Classes: List all values of the LDAP object class attribute for users in LDAP, separated by commas.
- Search Scope: The Search Scope determines the level of the LDAP search within the directory. There are two available options:
- One Level: The search applies only to users in the DNs specified by the User DNs.
- Subtree: The search applies to the entire subtree, meaning it will include all descendants of the specified DN.
- LDAP User Filter: The LDAP User Filter allows for additional filtering of users from the provided User DN. By default, the filter
objectClass=*is used. You can specify a custom filter, ensuring it begins with(and ends with). This enables more granular filtering of users from the LDAP directory. - Pagination: The Pagination option indicates whether the LDAP server supports pagination. Pagination enables the server to return results in multiple pages, reducing the load on the server and improving performance when dealing with large datasets.
- Synchronization Settings
- Batch Size for User Sync: The Batch Size for User Sync defines the number of users to be imported from the LDAP server to the Identity Provider in a single transaction. This helps optimize the synchronization process by controlling the size of each batch and minimizing resource consumption during user import.
- Periodic Full Sync (Optional): Enable to periodically perform a full synchronization of LDAP users to IDP.
- Full Sync Period: Period for full synchronization in seconds.
- Periodic changed users sync (Optional): Enable to periodically synchronize changed or newly created LDAP users to IDP.
- Changed Sync Period: Period for synchronization of changed or newly created LDAP users in seconds.
- General Options
- Clicking Save adds the LDAP provider to the user federation page.
The current version of vuSmartMaps supports adding only one LDAP Provider.
Enabling/Disabling LDAP Provider
On the User Federation page, a radio button allows you to enable/disable the LDAP provider.
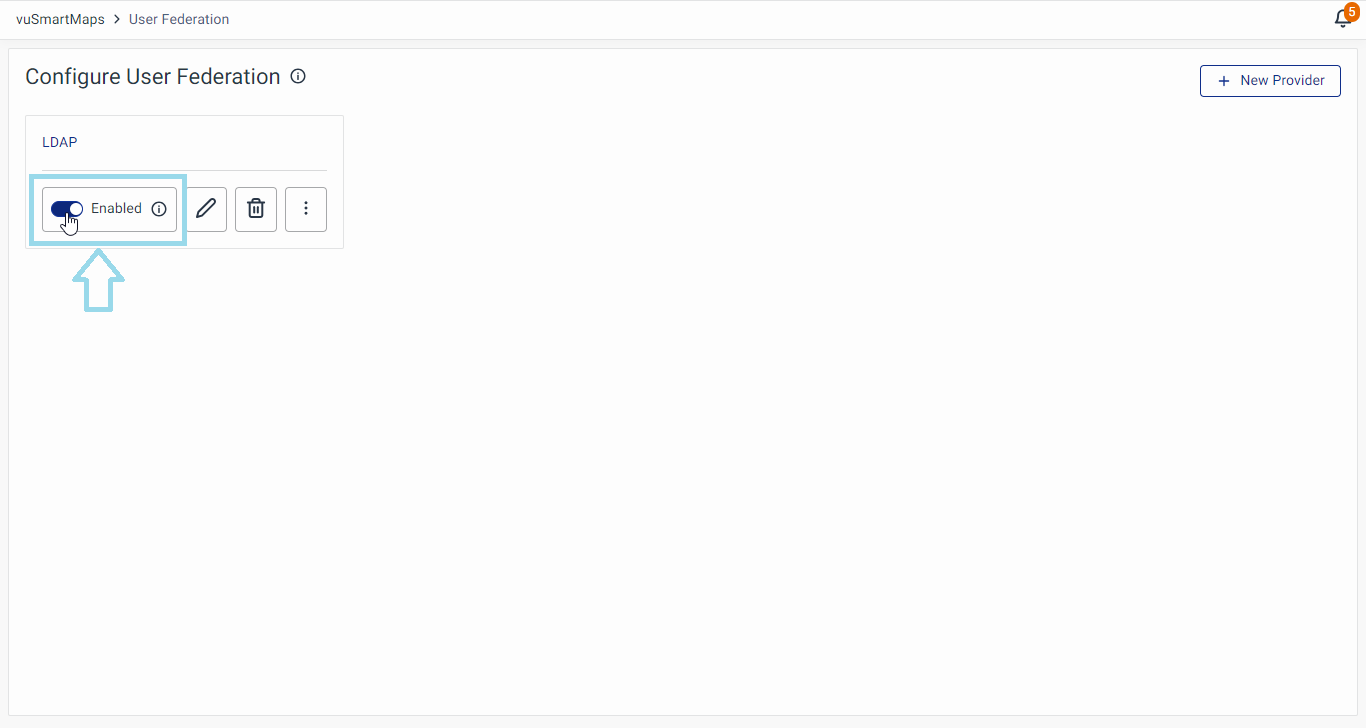
The LDAP provider is enabled by default after the initial addition in the user federation module.
Viewing LDAP Configuration
- Clicking on the provider's name navigates you to a page displaying all LDAP-related configuration settings in the Settings tab.
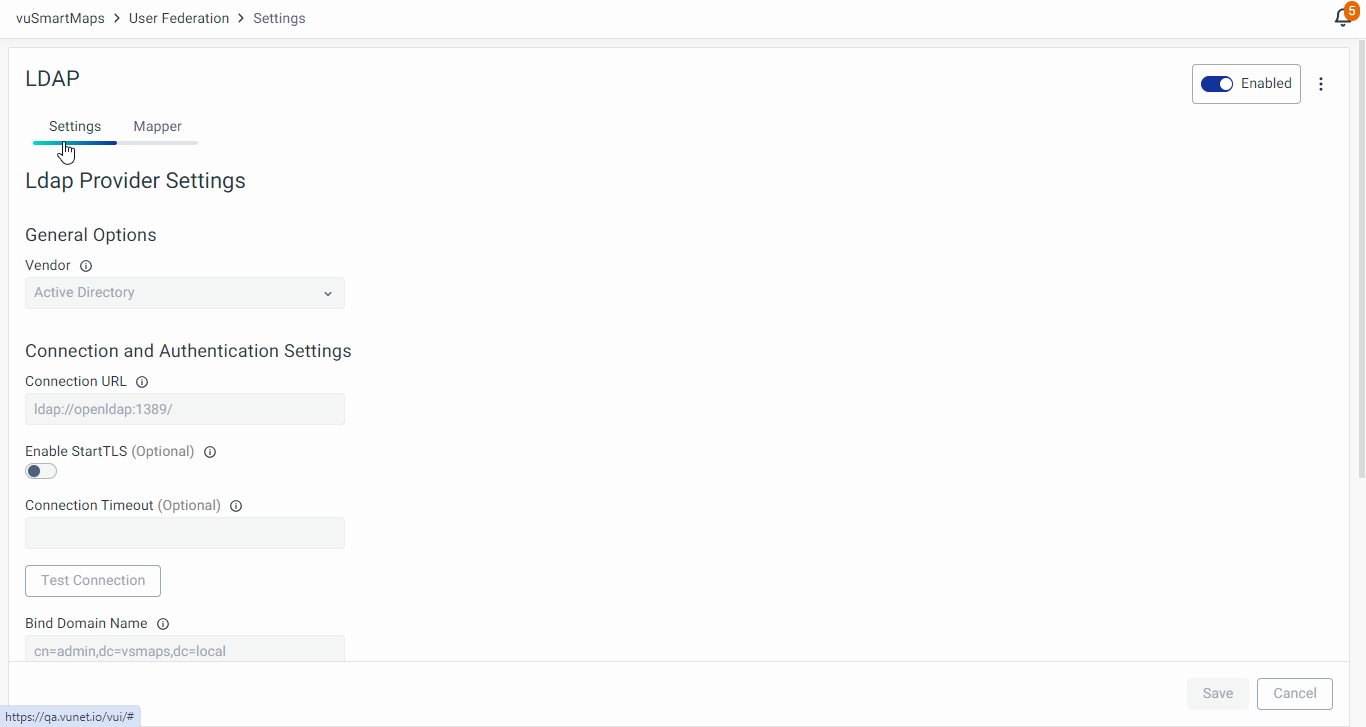
- Enable/Disable LDAP Server: Toggle using the radio button.
- Sync Users: Options include Sync changed users, Sync all users, and Remove imported users.
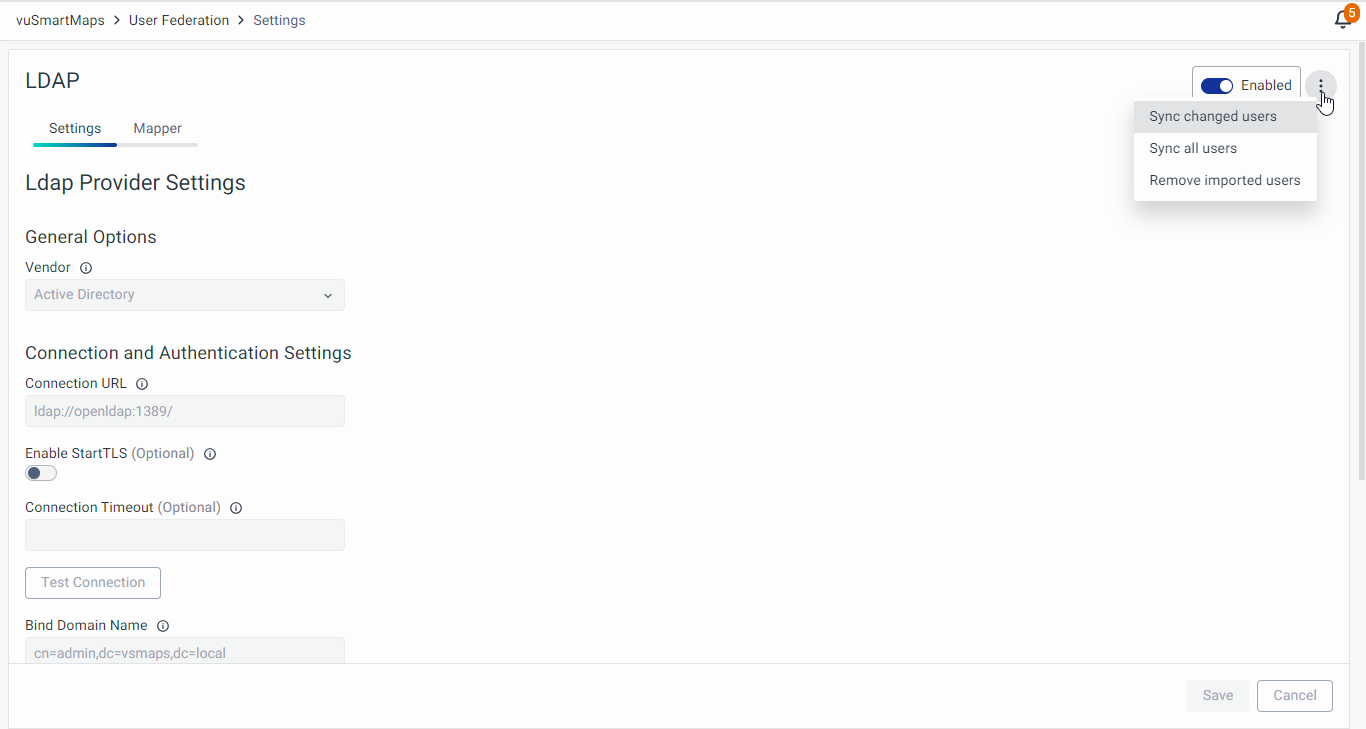
Editing LDAP Configuration
- To edit the LDAP configuration, click the Edit icon on the user federation page.
- Make necessary edits in the LDAP Provider settings.
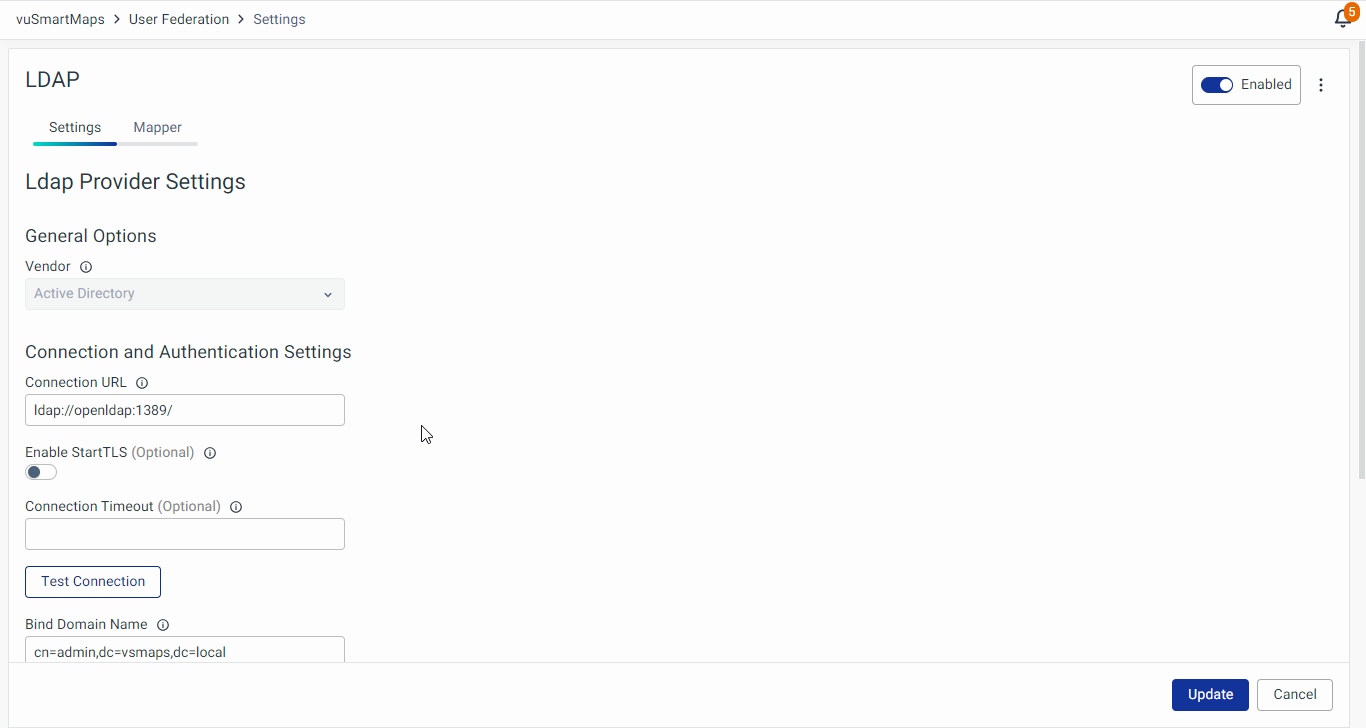
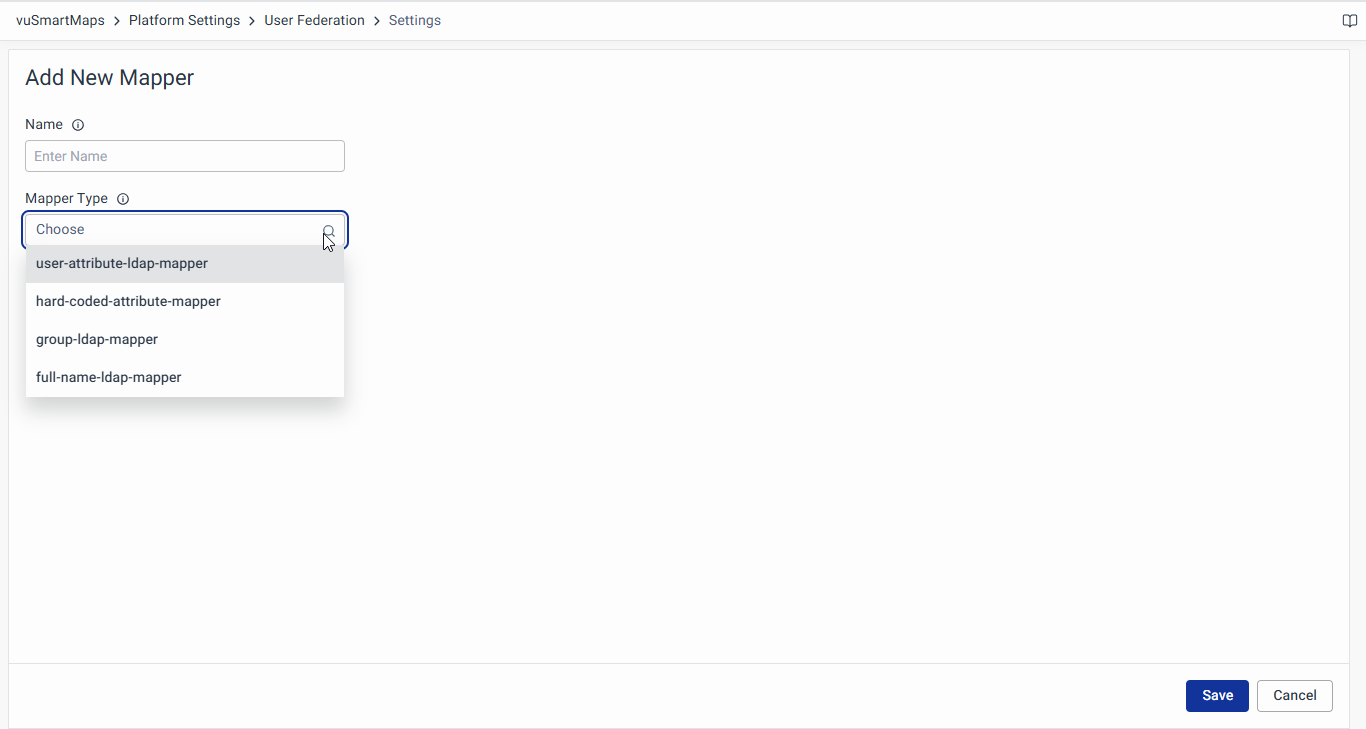
Adding a New Mapper
To integrate LDAP effectively, mappers help translate user attributes, roles/groups from LDAP into vuSmartMaps. Different types of mappers define how user data is processed.
- To add a new mapper, navigate to the Mapper tab. And click on the + New Mapper button.
- Provide all the required information related to the mapper.
- Name: Name of the mapper.
- Mapper Type: Used to map a single attribute from the LDAP user to the attribute in the identity provider database.
- User Attribute LDAP Mapper: Maps attributes from LDAP user to IDP user attributes.
- Hardcoded Attribute Mapper: Hardcode a value to a user attribute.
- Group LDAP Mapper: Maps group mappings from LDAP to identity provider.
- Full Name LDAP Mapper: Maps full name of user to first name & last name.
User Attribute LDAP Mapper
The User Attribute LDAP Mapper allows specific user attributes from LDAP to be mapped to the corresponding fields in vuSmartMaps. This ensures that user data such as email addresses, job titles, or department names are correctly synchronized between LDAP and vuSmartMaps.
Use Case
This mapper is used when organizations want to ensure that user attributes in LDAP are consistently reflected in vuSmartMaps. It is useful for synchronizing commonly used attributes such as email (mail), common name (cn), surname (sn), or phone number (telephoneNumber).
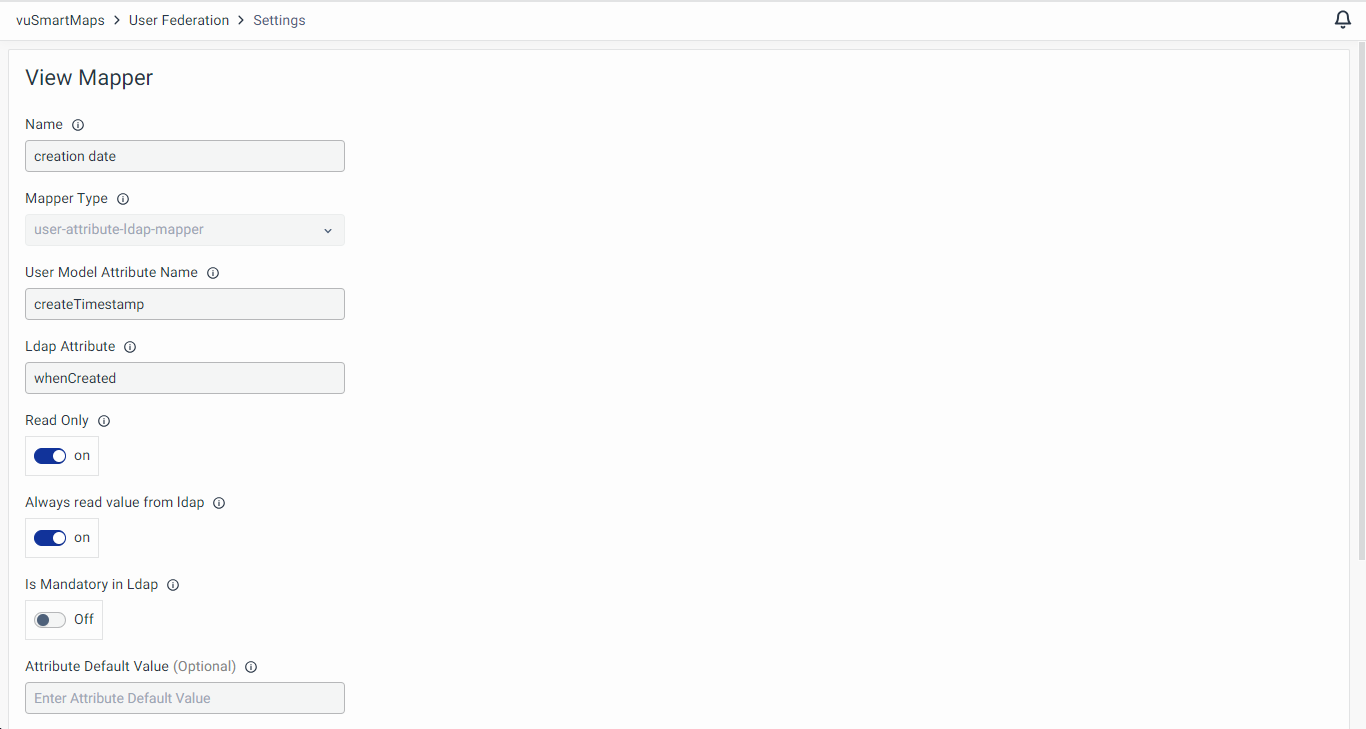
Configuration Fields
- User Model Attribute Name: Specifies the attribute in vuSmartMaps where the mapped LDAP attribute value will be stored.
- LDAP Attribute: Defines the name of the attribute in LDAP that holds the corresponding user data.
- Read Only (On/Off): If enabled, the attribute value is imported from LDAP but cannot be modified in vuSmartMaps.
- Always Read Value from LDAP (On/Off): When enabled, this setting ensures that the attribute value is always retrieved from LDAP rather than being stored in vuSmartMaps.
- Is Mandatory in LDAP (On/Off): Defines whether the attribute is required in LDAP. If enabled, a missing value could lead to errors during synchronization.
- Attribute Default Value (Optional): Specifies a default value that will be used if the attribute does not exist in LDAP.
- Force a Default Value (On/Off): When enabled, forces a default value to be applied even if no value is provided in LDAP.
- Is Binary Attribute (On/Off): If enabled, the attribute is treated as binary data, ensuring proper encoding and storage.
Use this mapper when attributes such as email, displayName, or phoneNumber need to be kept in sync between LDAP and vuSmartMaps.
Hardcoded Attribute Mapper
The Hardcoded Attribute Mapper allows administrators to assign a fixed value to a specific user attribute in vuSmartMaps. This is useful when a particular attribute should have the same value for all imported users, regardless of their LDAP information.
Use Case
This mapper is ideal when organizations want to enforce a predefined attribute value for all users, such as setting the employeeType to Contractual or department to IT. This ensures uniformity across user records within vuSmartMaps.
Configuration Fields
- User Model Attribute Name: Specifies the attribute in vuSmartMaps that will receive the hardcoded value.
- Attribute Value: The fixed value assigned to the specified attribute.
Use this mapper when all users should have the same default attribute value, ensuring consistency in user attributes across the system.
Group LDAP Mapper
The Group LDAP Mapper is used to map groups from LDAP to vuSmartMaps roles, ensuring that group structures in LDAP are mirrored within vuSmartMaps.
Configuring the Group LDAP Mapper is required only for Scenario 3, where groups from LDAP need to be imported into vuSmartMaps.
Use Case
This mapper is essential when organizations use LDAP groups for role-based access control (RBAC). It allows group-to-role synchronization, ensuring that users retain appropriate permissions within vuSmartMaps based on their LDAP group memberships.
Configuration Fields
- LDAP Groups DN: Specifies the distinguished name (DN) where the LDAP groups are stored.
- Group Name LDAP Attribute: Defines the attribute used for naming LDAP groups (e.g.,
cn). - Group Object Classes (Optional): Defines the LDAP object classes used for group identification (e.g.,
groupOfNames). - Preserve Group Inheritance (On/Off): If enabled, maintains LDAP group hierarchy when synchronizing with vuSmartMaps.
- Ignore Missing Groups (On/Off): If enabled, ignores missing groups in the hierarchy instead of treating them as errors.
- Membership LDAP Attribute (Optional): Defines the attribute in LDAP that stores user-group relationships (e.g.,
member). - Membership Attribute Type (Optional): Specifies whether group membership is stored as a distinguished name (DN) or a unique identifier (UID).
- Membership User LDAP Attribute: Defines the user attribute in LDAP that corresponds to the group membership mapping.
- LDAP Filter (Optional): Allows administrators to define a custom filter to limit imported groups.
note
You can set an LDAP Filter to define the common name as
Vunet-*to ensure that only roles with theVunet-prefix are imported. - Users Group Retrieve Strategy: Defines how groups are retrieved:
LOAD_GROUPS_BY_MEMBER_ATTRIBUTE: Retrieves groups by querying LDAP for member attributes.GET_GROUPS_FROM_USER_MEMBEROF_ATTRIBUTE: Retrieves groups from the memberOf attribute in the user entry.LOAD_GROUPS_BY_MEMBER_ATTRIBUTE_RECURSIVELY: Used for recursive retrieval of groups in Active Directory.
- Member of LDAP Attribute: Used when
GET_GROUPS_FROM_USER_MEMBEROF_ATTRIBUTEis selected. Defines the LDAP attribute that contains group membership information (default:memberOf). - Mapped Group Attributes (Optional): Specifies additional group attributes to be mapped in vuSmartMaps.
Use this mapper to synchronize LDAP groups with vuSmartMaps roles, ensuring seamless role-based access control.
Full Name LDAP Mapper
The Full Name LDAP Mapper is used to extract the full name of a user from LDAP and split it into first name and last name fields in vuSmartMaps.
Use Case
This mapper is useful when LDAP stores the user's full name as a single attribute (e.g., cn), and vuSmartMaps requires it to be separated into first and last name fields for consistency in user data representation.
Configuration Fields
- LDAP Full Name Attribute: Specifies the LDAP attribute that contains the full name of the user (e.g.,
cn).
Use this mapper when the common name (cn) attribute in LDAP contains both first and last names, and you need to store them separately in vuSmartMaps.
Viewing Mapper
Click on a mapper's name to view specific details.
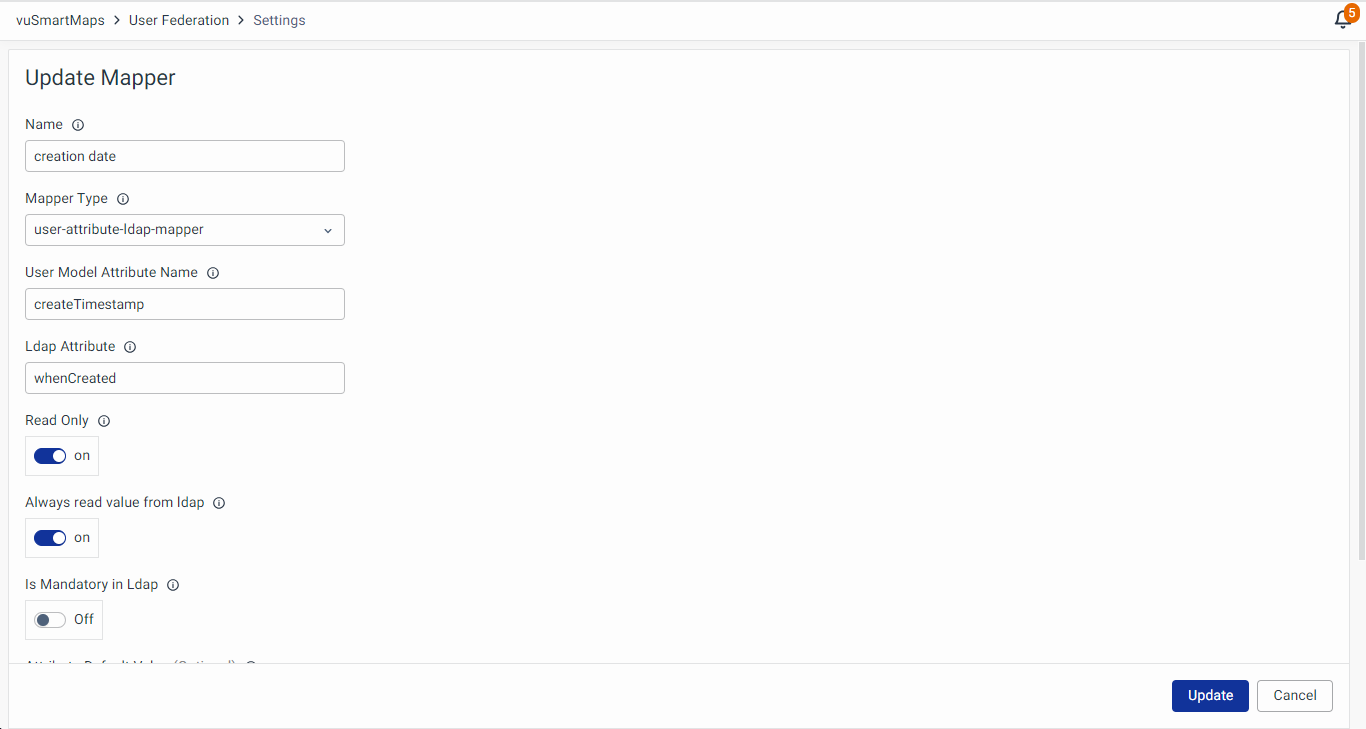
Editing the Mapper
To edit the existing mapper, click on the Edit icon across that respective mapper and edit the configuration as required.
Deleting the Mapper
To remove the existing mapper from the user federation page, click on the Delete icon across the respective mapper. Accepting the warning by clicking on the Delete button shall remove this mapper.
Deleting LDAP Configuration
- To delete the existing LDAP configuration, click the Delete icon on the user federation landing page.
- Accept the warning message to remove the LDAP configuration.
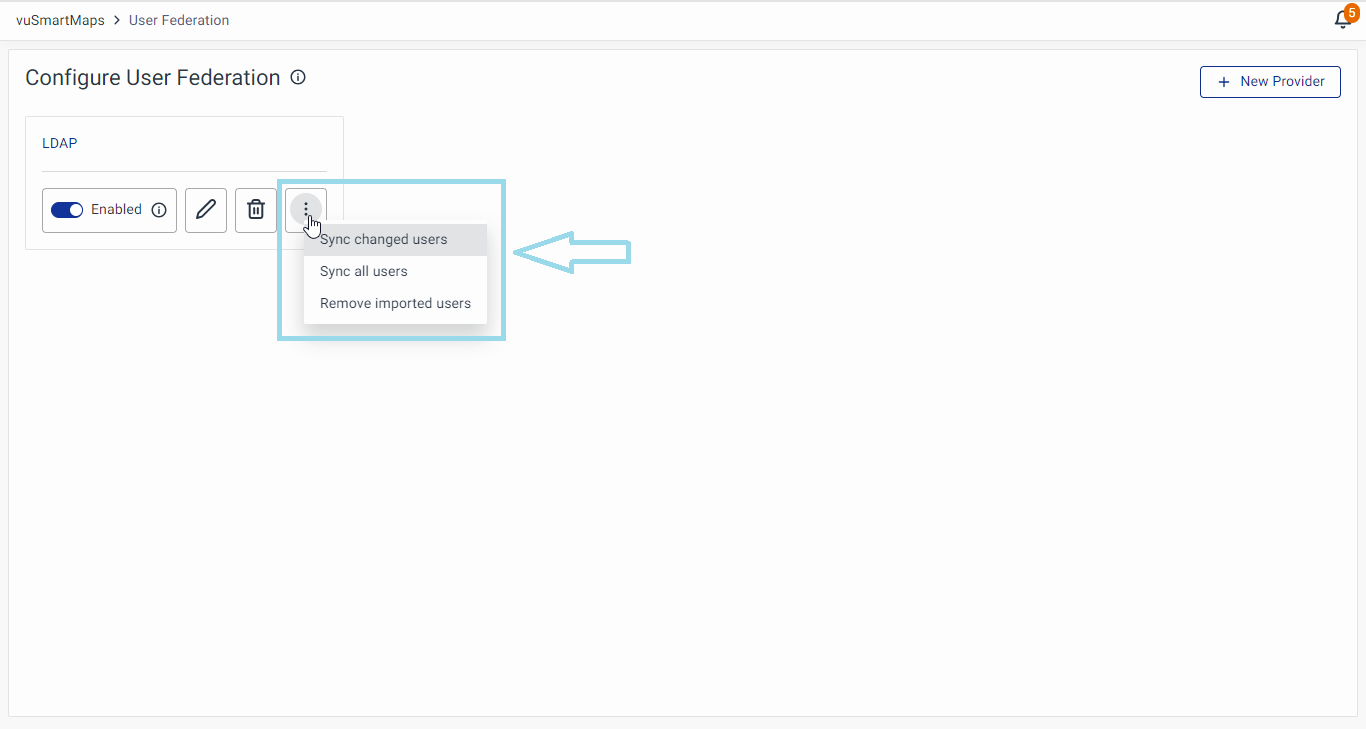
Syncing Users with LDAP Server
You can sync users with the options available, as required.
- Sync changed users
- Sync all users
- Remove Imported Users
To view the users added by the LDAP provider, navigate to the User Management module.

When LDAP is configured and synchronization occurs, all LDAP users are imported into the system. However, by applying the Vunet-* filter to the group, only the groups with this prefix will be pulled. Additionally, in the user management module, all roles with the Vunet- prefix will be listed.
Assigning Permissions to LDAP Roles
Administrators can assign permissions to LDAP roles within vuSmartMaps to ensure appropriate access control for different users.
Steps to Assign or Modify Permissions
- Navigate to the User Management module and select the Roles tab.
- Locate the Role for which permissions need to be assigned or modified.
- Click on Edit Role Permissions to open the permission configuration modal.
- In the modal, assign or modify the necessary permissions as required.
- Click Save to apply the changes.
Object-Level Permissions
For specific objects such as Dashboards, Alerts, and Reports, ensure that Data Access Policies are correctly configured to grant appropriate access rights.
To modify object-level permissions:
- Navigate to the respective module (e.g., Dashboards, Alerts, Reports).
- Locate the object and open the permissions settings.
- Assign or edit access permissions based on organizational requirements.
- Save the changes to enforce the new permissions.
Example: For modifying Dashboard Permissions, detailed steps are available in the Dashboard Module documentation.
Signing in with LDAP Provider
Once successfully configured, logging in through the LDAP provider is as straightforward as a standard login, using default username/password forms for authentication.
